Tentacle
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2010) |
A tentacle or bothrium (plural: bothria) is one of usually two or more elongated flexible organs present in animals, especially invertebrates. The term may also refer to the hairs of the leaves of some insectivorous plants. Usually, tentacles are used for feeding, feeling and grasping. Anatomically, they work like other muscular hydrostats. The word tentillum is a diminutive, but although it literally means "a little tentacle", it usually refers, irrespective of size, to a side branch of a larger tentacle. In some cases such tentilla are specialised for particular functions; for example, in the Cnidaria tentilla usually bear cnidocytes,[1] whereas in the Ctenophora they usually bear collocytes.[2][3]
Tentacles in animals
Invertebrates
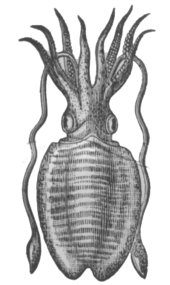
The phylum Mollusca includes many species with muscular hydrostats in the form of tentacles and arms. Octopuses do have tentacles but are rather known as arms. Tentacles are distinguished in this context as being longer than arms, with suckers at their tips only. Squid and cuttlefish have eight arms like octopuses, and two extra flexible tentacles.
The tentacles of the giant squid and colossal squid have powerful suckers and pointed teeth at the ends. The teeth of the giant squid resemble bottle caps, and function like small, circular saws; while the tentacles of the colossal squid wield two long rows of swiveling, tri-pointed hooks.


Snails are another class of Mollusca. They have less elaborate tentacles than the cephalopods. Pulmonate land snails usually have two sets of tentacles on the head: the upper pair have an eye at the end; the lower pair are for olfaction. Both pairs are fully retractable. Some marine snails such as the abalone and the top snails, Trochidae, have numerous small tentacles around the edge of the mantle. These are known as pallial tentacles.
Cnidarians, which include among others the jellyfishes, are another phylum with many tentacled specimens. Cnidarians often have huge numbers of cnidocytes on their tentacles. Cnidocytes are cells containing a coiled thread-like structure called a nematocyst, fired at potential prey.
Many species of the jellyfish-like ctenophores have two tentacles, while some have none. Their tentacles have adhesive structures called colloblasts or lasso cells. These cells burst open when prey comes in contact with the tentacle; sticky threads released from each of the colloblasts then captures food.
The tentacles of the Lion's mane jellyfish can reach 120 feet (37 meters).
Bryozoa (moss animals) are tiny creatures with a ring of tentacles surrounding the mouth.
Amphibians
Some wormlike amphibians have tentacles. The caecilians have two tentacles at their heads, which are probably used for smell.
Mammals
The star-nosed mole, Condylura cristata, possesses nasal tentacles which are mobile and extremely sensitive, helping the animal to find its way about the burrow and detect prey.
Tentacles in plants

In carnivorous plants, tentacles refer to the stalked glands of the upper surface of the leaves.
On a sundew plant, they are hairlike projections with a drop of nectar-like glue which attract insects. When an insect is captured, the tentacles bend inward and the leaf rolls together as shown in the picture. The tentacles then secrete enzymes to dissolve and digest the insect.
See also
References
- ^ http://species-identification.org/species.php?species_group=zsao&selected=definitie&menuentry=woordenlijst&record=tentilla
- ^ Harmer, Sir Sidney Frederic; Shipley, Arthur Everett et alia: The Cambridge natural history Volume 1, Protozoa, Porifera, Coelenterata, Ctenophora, Echinodermata. Macmillan Company 1906
- ^ Mackie G.O., Mills C.E., Singla C.L.: Structure and function of the prehensile tentilla of Euplokamis (Ctenophora, Cydippida). Zoomorphology (1988) 107:319-337
