Dew point

The dew point or dewpoint of a given parcel of air is the temperature to which the parcel must be cooled, at constant barometric pressure, for the water vapor component to condense into water, called dew. When the dew point temperature falls below freezing it is called the frost point as the water vapor no longer creates dew but instead creates frost or hoarfrost by deposition.
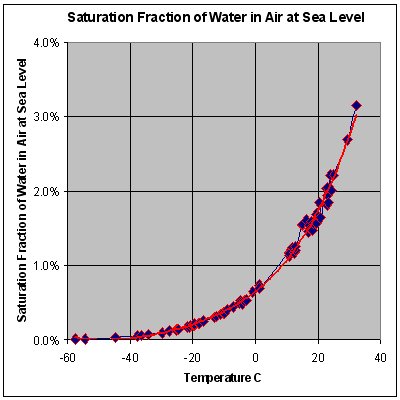
The graph to the right shows the maximum percentage of water vapor that can exist in air at sea level across a range of temperatures. Note that with higher temperatures the equilibrium partial pressure of water vapor increases thus more water evaporates. The behavior of water vapor does not depend on the presence of air. The formation of dew would occur at the dew point even if the only gas present were water vapor.
The dew point is associated with the relative humidity. A high relative humidity indicates that the dew point is closer to the current air temperature. If the relative humidity is 100%, the dew point will be equal to the current temperature. Given a constant dew point, when the temperature increases the relative humidity will decrease. It is for this reason that equatorial climates can have low relative humidity yet still feel uncomfortable.
Humans tend to react with discomfort to high dew points. Those accustomed to continental climates often begin to feel uncomfortable when the dew point reaches between 15 and 20 °C (59 to 68 °F). Most inhabitants of these areas will consider dew points above 21 °C (70 °F) to be oppressive.
Here is a formula to calculate the dew point in degrees Celsius to within ±0.4 °C. It is valid for
- 0 °C < T < 100 °C
- 0.01 < RH < 1.0
- 0 °C < Td < 50 °C
where
- T = temperature in degrees Celsius
- RH = is the relative humidity as a fraction (not percent)
- Td = the dew point temperature to be calculated
The formula is:
where
and
- a = 17.27
- b = 237.7 °C
- ln is the natural logarithm.
For a derivation of the above formula as well as an error estimation of it, see e.g. [1].
| Dew On Webs | Dew On plants |
|---|---|
| File:DewPointWetWeb.jpg | File:DamavandDew2.jpg |
| Mount Damavand - Iran | Mount Damavand - Iran |


