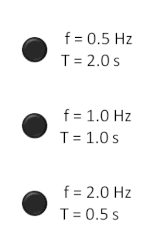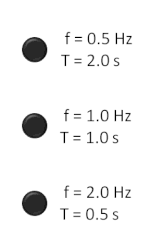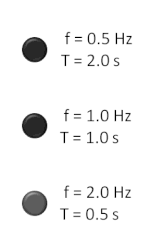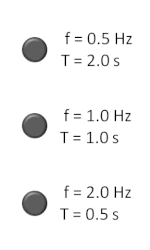Search results
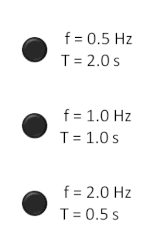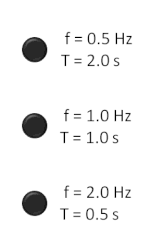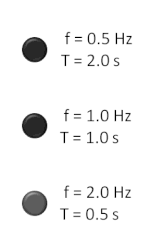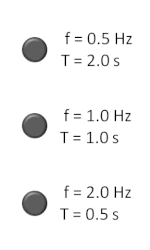 The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is...16 KB (1,687 words) - 05:29, 6 May 2024
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is...16 KB (1,687 words) - 05:29, 6 May 2024- The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k {\displaystyle k} , λ {\displaystyle \lambda...63 KB (8,353 words) - 10:34, 20 April 2024
 In physics, motion is when an object changes its position with respect to a reference point in a given time. Motion is mathematically described in terms...31 KB (3,797 words) - 14:17, 15 April 2024
In physics, motion is when an object changes its position with respect to a reference point in a given time. Motion is mathematically described in terms...31 KB (3,797 words) - 14:17, 15 April 2024 In electrical engineering, impedance is the opposition to alternating current presented by the combined effect of resistance and reactance in a circuit...32 KB (5,061 words) - 19:26, 7 April 2024
In electrical engineering, impedance is the opposition to alternating current presented by the combined effect of resistance and reactance in a circuit...32 KB (5,061 words) - 19:26, 7 April 2024 Fusion power is a proposed form of power generation that would generate electricity by using heat from nuclear fusion reactions. In a fusion process, two...194 KB (20,819 words) - 13:04, 14 May 2024
Fusion power is a proposed form of power generation that would generate electricity by using heat from nuclear fusion reactions. In a fusion process, two...194 KB (20,819 words) - 13:04, 14 May 2024 The solar mass (M☉) is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately 2×1030 kg. It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. It is...13 KB (1,536 words) - 01:57, 28 April 2024
The solar mass (M☉) is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately 2×1030 kg. It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. It is...13 KB (1,536 words) - 01:57, 28 April 2024- A muon (/ˈm(j)uːɑːn/ M(Y)OO-on; from the Greek letter mu (μ) used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric...46 KB (5,551 words) - 13:39, 2 May 2024
- The centimetre–gram–second system of units (CGS or cgs) is a variant of the metric system based on the centimetre as the unit of length, the gram as the...36 KB (3,468 words) - 11:54, 27 April 2024
 Hendrik Antoon Lorentz (/ˈlɒrənts/; 18 July 1853 – 4 February 1928) was a Dutch physicist who shared the 1902 Nobel Prize in Physics with Pieter Zeeman...46 KB (4,860 words) - 22:20, 10 May 2024
Hendrik Antoon Lorentz (/ˈlɒrənts/; 18 July 1853 – 4 February 1928) was a Dutch physicist who shared the 1902 Nobel Prize in Physics with Pieter Zeeman...46 KB (4,860 words) - 22:20, 10 May 2024 Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the...29 KB (3,363 words) - 01:46, 23 April 2024
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the...29 KB (3,363 words) - 01:46, 23 April 2024 A Faraday cage or Faraday shield is an enclosure used to block some electromagnetic fields. A Faraday shield may be formed by a continuous covering of...17 KB (2,000 words) - 02:41, 9 May 2024
A Faraday cage or Faraday shield is an enclosure used to block some electromagnetic fields. A Faraday shield may be formed by a continuous covering of...17 KB (2,000 words) - 02:41, 9 May 2024 The Zeeman effect (/ˈzeɪmən/; Dutch pronunciation: [ˈzeːmɑn]) is the effect of splitting of a spectral line into several components in the presence of...34 KB (5,064 words) - 04:12, 10 May 2024
The Zeeman effect (/ˈzeɪmən/; Dutch pronunciation: [ˈzeːmɑn]) is the effect of splitting of a spectral line into several components in the presence of...34 KB (5,064 words) - 04:12, 10 May 2024 A Type II supernova or SNII (plural: supernovae) results from the rapid collapse and violent explosion of a massive star. A star must have at least eight...48 KB (4,780 words) - 10:08, 20 April 2024
A Type II supernova or SNII (plural: supernovae) results from the rapid collapse and violent explosion of a massive star. A star must have at least eight...48 KB (4,780 words) - 10:08, 20 April 2024- Muon-catalyzed fusion (abbreviated as μCF or MCF) is a process allowing nuclear fusion to take place at temperatures significantly lower than the temperatures...28 KB (3,874 words) - 23:01, 16 March 2024