Search results
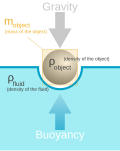 Buoyancy (/ˈbɔɪənsi, ˈbuːjənsi/), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In...27 KB (4,193 words) - 23:26, 8 April 2024
Buoyancy (/ˈbɔɪənsi, ˈbuːjənsi/), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In...27 KB (4,193 words) - 23:26, 8 April 2024- In condensed matter physics, an ultracold atom is an atom with a temperature near absolute zero. At such temperatures, an atom's quantum-mechanical properties...12 KB (1,467 words) - 07:26, 22 April 2024
 In photography and optics, a neutral-density filter, or ND filter, is a filter that reduces or modifies the intensity of all wavelengths, or colors, of...15 KB (1,676 words) - 04:11, 1 April 2024
In photography and optics, a neutral-density filter, or ND filter, is a filter that reduces or modifies the intensity of all wavelengths, or colors, of...15 KB (1,676 words) - 04:11, 1 April 2024- The innermost stable circular orbit (often called the ISCO) is the smallest marginally stable circular orbit in which a test particle can stably orbit...8 KB (1,227 words) - 08:42, 21 February 2024
- The Very Large Hadron Collider (VLHC) was a proposed future hadron collider planned to be located at Fermilab. The VLHC was planned to be located in a...5 KB (477 words) - 17:20, 5 March 2023
- Dieter Möhl (1936 — May 24, 2012) was a German accelerator physicist. Möhl worked at CERN and contributed substantially to the antiproton programme, the...1 KB (87 words) - 11:25, 7 April 2022
- Field cycling is a measurement method which uses variable magnetic fields to measure the magnetization of a sample. Fast field cycling is the same method...1 KB (132 words) - 00:44, 31 January 2024


