Jordan Rift Valley: Difference between revisions
→Demography: better sourcing needed |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
The Jordanian population of the valley is over 85,000 people,<ref name=Countrydata>{{cite web|title=Jordan|publisher=Country Data|accessdate=2007-07-10|url=http://www.country-data.com/cgi-bin/query/r-7380.html}}</ref> most of whom are farmers, and 80% of the farms in the Jordanian part of the valley are family farms no larger than 30 [[dunam]]s (3 ha, 7.4 ac).<ref>{{cite web|title=High tech may water Jordan Valley, but dry up family farming|author=Dana Charkasi|publisher=Jordan Times|date=31 August 2000|url=http://www.jordanembassyus.org/08312000008.htm}}</ref> |
The Jordanian population of the valley is over 85,000 people,<ref name=Countrydata>{{cite web|title=Jordan|publisher=Country Data|accessdate=2007-07-10|url=http://www.country-data.com/cgi-bin/query/r-7380.html}}</ref> most of whom are farmers, and 80% of the farms in the Jordanian part of the valley are family farms no larger than 30 [[dunam]]s (3 ha, 7.4 ac).<ref>{{cite web|title=High tech may water Jordan Valley, but dry up family farming|author=Dana Charkasi|publisher=Jordan Times|date=31 August 2000|url=http://www.jordanembassyus.org/08312000008.htm}}</ref> |
||
Some 47,000 [[Palestinians]] live in the part of the valley that lies in the West Bank in about twenty permanent communities, most of them reside in the city of [[Jericho]]. Thousands of [[Bedouins]] also live in temporary communities.<ref name=Btselem>{{cite web|title=Israel has de facto annexed the Jordan Valley|author=[[B'tselem]]|date=13 February 2006|url=http://www.btselem.org/English/Settlements/20060213_Annexation_of_the_Jordan_Valley.asp}}</ref> |
Some 47,000 [[Palestinians]] live in the part of the valley that lies in the West Bank in about twenty permanent communities, most of them reside in the city of [[Jericho]]. Thousands of [[Bedouins]] also live in temporary communities.<ref name=Btselem>{{cite web|title=Israel has de facto annexed the Jordan Valley|author=[[B'tselem]]|date=13 February 2006|url=http://www.btselem.org/English/Settlements/20060213_Annexation_of_the_Jordan_Valley.asp}}</ref>{{fact}} |
||
[[File:PikiWiki Israel 9831 Geography of Israel.jpg|thumb|Date palms of Kibbutz [[Gesher]], Jordan Rift Valley]] |
[[File:PikiWiki Israel 9831 Geography of Israel.jpg|thumb|Date palms of Kibbutz [[Gesher]], Jordan Rift Valley]] |
||
About 11,000 [[Israelis]] live in 17 [[kibbutzim]] that form part of the [[Emek HaYarden Regional Council]] in Israel,<ref>[http://bohabayta.com/meshakim/RC_Emek_Hayarden/default_eng.asp About Emek Hayarden R.C.]</ref> while an additional 7,500 live in twenty-six [[Israeli settlements]] and five [[Nahal]] encampments that have been established in the part of the Jordan Valley that lies in the West Bank.{{fact}} |
About 11,000 [[Israelis]] live in 17 [[kibbutzim]] that form part of the [[Emek HaYarden Regional Council]] in Israel,<ref>[http://bohabayta.com/meshakim/RC_Emek_Hayarden/default_eng.asp About Emek Hayarden R.C.]</ref> while an additional 7,500 live in twenty-six [[Israeli settlements]] and five [[Nahal]] encampments that have been established in the part of the Jordan Valley that lies in the West Bank.{{fact}} |
||
Revision as of 06:12, 10 December 2013
It has been suggested that this article be merged with Jordan Valley (Middle East). (Discuss) Proposed since November 2013. |

The Jordan Rift Valley (Arabic: الغور Al-Ghor or Al-Ghawr; Hebrew: בקעת הירדן Bik'at HaYarden) is an elongated depression located in modern-day Israel, Jordan and the Palestinian territories. This geographic region includes the Jordan River, Jordan Valley, Hula Valley, Lake Tiberias and the Dead Sea, the lowest land elevation on Earth. The valley continues to the Red Sea, incorporating Arabah and the shorelines of the Gulf of Aqaba.
History and physical features
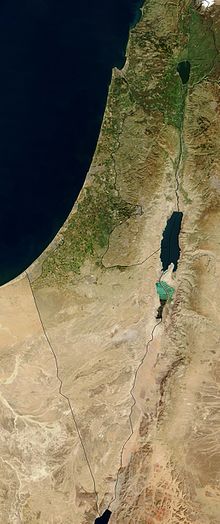
The Jordan Rift Valley was formed many millions of years ago in the Miocene epoch (23.8 - 5.3 Myr ago) when the Arabian tectonic plate moved northward and then eastward away from Africa. One million years later, the land between the Mediterranean and the Jordan Rift Valley rose so that the sea water stopped flooding the area.
The geological and environmental evolution of the valley since its inception in the Oligocene can be seen in a variety of sedimentary and magmatic rock units, preserved as continuous sequences in the deeper basins. The outcropping formations around the basins represent alternating deposition and erosion phases.[1]
The lowest point in the Jordan Rift Valley is in the Dead Sea, the lowest spot of which is 790 metres below sea level. The shore of the Dead sea is the lowest land on earth, at 400 meters (about 1300 feet) below sea level. Rising sharply to almost 1,000 meters (almost 3,300 feet) in the west, and similarly in the east, the rift is a significant topographic feature over which a few narrow paved roads and difficult mountain tracks lead.[2] The valley north of the Dead Sea has long been a site of agriculture because of water available from the Jordan River and numerous springs located on the valley's flanks.
Dead Sea Transform
The plate boundary which extends through the valley is variously called the Dead Sea Transform or Dead Sea Rift. The boundary separates the Arabian plate from the African plate, connecting the divergent plate boundary in the Red Sea (the Red Sea Rift) to the East Anatolian Fault in Turkey.[3]
The interpretation of the tectonic regime that led to the development of the Dead Sea Transform is highly contested. Some consider it as a transform fault that accommodates a 105 km northwards displacement of the Arabian plate,[4] and trace its structural evolution to the early Miocene. Others presume that the Rift is an incipient oceanic spreading center, the northern extension of the Red Sea Rift,[5] and the displacement along it is oblique, with approximately 10–15 km of extension in addition to the more substantial left lateral (sinistral) strike-slip. The evolution of the rift, according to this latter model, started in the late Miocene with the linear series of basins that propagated gradually along their axes to form the present rift valley.[6] The elucidation of the nature of the Dead Sea Transform/Rift is a matter of ongoing study and discussion.
Demography
The Jordanian population of the valley is over 85,000 people,[7] most of whom are farmers, and 80% of the farms in the Jordanian part of the valley are family farms no larger than 30 dunams (3 ha, 7.4 ac).[8]
Some 47,000 Palestinians live in the part of the valley that lies in the West Bank in about twenty permanent communities, most of them reside in the city of Jericho. Thousands of Bedouins also live in temporary communities.[9][citation needed]

About 11,000 Israelis live in 17 kibbutzim that form part of the Emek HaYarden Regional Council in Israel,[10] while an additional 7,500 live in twenty-six Israeli settlements and five Nahal encampments that have been established in the part of the Jordan Valley that lies in the West Bank.[citation needed] Prior to the 1967 Six-Day War, the valley's Jordanian side was home to about 60,000 people largely engaged in agriculture and pastoralism.[7] By 1971, the population had declined to 5,000 as a result of the war and the 1970-71 conflict between the Palestinian guerrillas and the Jordanian armed forces.[7] Investments by the Jordanian government in the region allowed the population to rebound to over 85,000 by 1979.[7]
Since the end of the 1967 war, every Israeli government has considered the western Jordan Valley to be the eastern border of Israel with Jordan.[9] The 1994 peace treaty between Israel and Jordan defines the international border between the countries on the Jordan river in the center of the Jordan valley.

Agriculture
The Jordan River rises from several sources, mainly the Anti-Lebanon Mountains in Syria. It flows down into the Sea of Galilee, 212 meters below sea level, and then drains into the Dead Sea.[11] South of the Dead Sea, the Jordan Valley turns into the hot, dry Arabah valley.[11]
The Jordan Valley is several degrees warmer than adjacent areas, and its year-round agricultural climate, fertile soils and water supply made it a site for agriculture dating to about 10,000 years ago. By about 3000 BCE, produce from the valley was being exported to neighboring regions.[11] The area's fertile lands were chronicled in the Hebrew Bible, where it was the site of several miracles for the people of Israel, such as the Jordan River stopping its flow to allow the Jewish people, led by the Ark of the Covenant, to pass over. The Jordan River is revered by Christians as the place where John the Baptist baptized Jesus Christ.[11]
In the last few decades, modern methods of farming have vastly expanded the agricultural output of the area.[11] The construction of the East Ghor Canal by Jordan in 1950s (now known as the King Abdullah Canal), which runs down the east bank of the Jordan Valley for 69 kilometers, has brought new areas under irrigation.[11] The introduction of portable greenhouses has brought about a sevenfold increase in productivity, allowing Jordan to export large amounts of fruit and vegetables year-round.[11]
References
- ^ The Jordan Rift Valley, [[Tel Aviv University
- ^ David Eshel (3 May 2006). "Increasing Importance of the Jordan Rift Buffer". Defense Update.
- ^ The Geophysical Institute
- ^ e.g. Freund et al., 1970, The Shear along the Dead Sea Rift, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences Vol. 267, No. 1181 and Joffe and Garfunkel, 1987, Plate Kinematics of the Circum Red-Sea - A Reevaluation, Tectonophysics v. 141 (1-3): 5-22
- ^ Horowitz, Aharon, The Jordan Rift Valley, Taylor & Francis, 2001 ISBN 978-90-5809-351-6
- ^ Mart, Y., 1994, The Dead Sea rift, a leaky transform fault or an oblique spreading center: a short review, Africa Geosci. Rev. 1, 567–578
- ^ a b c d "Jordan". Country Data. Retrieved 2007-07-10. Cite error: The named reference "Countrydata" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Dana Charkasi (31 August 2000). "High tech may water Jordan Valley, but dry up family farming". Jordan Times.
- ^ a b B'tselem (13 February 2006). "Israel has de facto annexed the Jordan Valley".
- ^ About Emek Hayarden R.C.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Touristic Sites: The Jordan Valley". The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan.
32°19′02″N 35°34′12″E / 32.31722°N 35.57000°E
![]() Media related to Jordan Rift Valley at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Jordan Rift Valley at Wikimedia Commons
