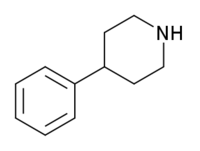
4-Phenylpiperidine
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-Phenylpiperidine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.130 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H15N | |
| Molar mass | 161.248 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
4-Phenylpiperidine is a chemical compound. It features a benzene ring bound to a piperidine ring.
4-Phenylpiperidine is the base structure for a variety of opioids, such as pethidine (meperidine), ketobemidone, alvimopan, loperamide, and diphenoxylate. Other pharmaceutical drugs derived from 4-phenylpiperdine include haloperidol, ropitoin, vesamicol, enefexine, and Altapizone.
A related compound is 4-benzylpiperidine, in which the rings are separated by a methylene bridge.
See also
