Province of Brabant
Brabant | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Country | |
| Capital | Brussels |

The Province of Brabant (/brəˈbænt/, also US: /brəˈbɑːnt, ˈbrɑːbənt/,[1][2][3] Dutch: [ˈbraːbɑnt] ) was a province in Belgium from 1830 to 1995. It was created in 1815 as South Brabant, part of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands.[4] In 1995, it was split into the Dutch-speaking Flemish Brabant, the French-speaking Walloon Brabant and the bilingual Brussels-Capital Region.[5]
History
United Kingdom of the Netherlands
After the defeat of Napoleon in 1815, the United Kingdom of the Netherlands was created at the Congress of Vienna, consisting of territories which had been added to France by Napoleon: the former Dutch Republic and the Southern Netherlands. In the newly created kingdom, the former French département Dyle became the new province of South Brabant, distinguishing it from Central Brabant (later Antwerp province); and from North Brabant (now part of the Netherlands), all named after the former Duchy of Brabant.
The provincial governors during this time were:
- 1815–1818: François Joseph Charles Marie de Mercy-Argenteau
- 1818–1823: Philippe d'Arschot Schoonhoven
- 1823–1828: Leonard du Bus de Gisignies
- 1828–1830: Hyacinthe van der Fosse
Belgium
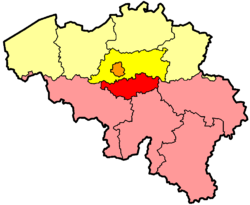
After the Belgian Revolution of 1830, the Southern Netherlands (including South and Central Brabant) became independent as Belgium and later also Luxembourg. The province was then renamed simply Brabant and became the central province of Belgium, with its capital city Brussels. The province contained three arrondissements: Brussels, Leuven and Nivelles.
In 1961–1963 the language border was established, from which the province was divided into a Dutch-speaking region, a French-speaking region and the bilingual Brussels. The Brussels arrondissement was split to this end. In 1989, Brussels-Capital Region was created, but the region was still part of the province of Brabant. In 1995, the province of Brabant was split into the Dutch-speaking Flemish Brabant, the French-speaking Walloon Brabant and the bilingual Brussels-Capital Region. The Brussels-Capital Region exercises the powers of a Province on its own territory.
Demographics
As comparison, the current two provinces of Brabant, together with Brussels, had 2,621,275 inhabitants in January 2011.
Number of inhabitants x 1000

- Source: NIS
- 1806 till 1970: census
- 1980 and 1990: number of inhabitants on 1 January
- 1994: number on 31 December
See also
References
- ^ "Brabant". Collins English Dictionary. HarperCollins. Retrieved May 29, 2019.
- ^ "Brabant" (US) and "Brabant". Oxford Dictionaries UK English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. n.d. Retrieved May 29, 2019.
- ^ "Brabant". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Merriam-Webster. Retrieved May 29, 2019.
- ^ Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- ^ "Administratief Arrondissement Brussel-Hoofdstad". Archived from the original on 2016-08-29. Retrieved 2011-09-17.

