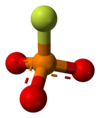
Monofluorophosphate
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Fluoro-dioxido-oxo-λ5-phosphane
| |||
| Other names
Fluorophosphate, Phosphorofluoridat, Phosphorofluoridate
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| PO3F2– | |||
| Molar mass | 97.971 g/mol | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Monofluorophosphate is an anion with the formula PO3F2−, which is a phosphate group with one oxygen atom substituted with a fluoride atom. The charge of the ion is −2. The ion resembles sulfate in size, shape and charge, and can thus form compounds with the same structure as sulfates. These include Tutton's salts and langbeinites. The most well-known compound of monofluorophosphate is sodium monofluorophosphate, commonly used in toothpaste.
Related ions include difluorophosphate (PO
2F−
2) and hexafluorophosphate (PF−
6).[1] The related neutral molecule is phosphenic fluoride PO2F.
Organic derivatives can be highly toxic and include diisopropyl fluorophosphate. Some of the Novichok agents are monofluorophosphate esters. Names are given to these by naming the groups attached as esters and then adding "fluorophosphonate" to the end of the name. Two organic groups can be attached. Other related nerve gas substances may not be esters, and instead have carbon-phosphorus or nitrogen-phosphorus bonds. The organic fluorophosphonates react with serine esterases and serine proteases irreversibly. This prevents these enzymes from functioning. Such an important enzyme is acetylcholinesterase as found in most animals.[2] Some of the organic esters are detoxified in mammals by an enzyme in the blood and liver called paraoxonase PON1.[3]
Willy Lange from Berlin discovered sodium monofluorophosphate in 1929. He fruitlessly tried to make monofluorophosphoric acid. However, he did discover the highly toxic organic esters. Following this discovery various nerve gases like sarin were developed.
Fluorophosphate glasses are low melting point kinds of glass which are mixtures of fluoride and phosphate metal compounds. For example, the composition 10% SnO, 40% SnF2, 50% P2O5 forms a glass melting about 139 °C. PbO and PbF2 can lower the melting temperature, and increase water resistance.[4] These glasses can also be coloured by various other elements, and organic dyes.
Production
Hydrolysis of difluorophosphate with an alkali produces monofluorophosphate.
- PO
2F−
2 + 2 MOH → M2PO3F + H2O + F−
Industrial production is by reaction of a fluoride with a metaphosphate.
- MF + MPO3 → M2PO3F
Disodium hydrogen phosphate or tetrasodium pyrophosphate can react with hydrogen fluoride to form the sodium salt.
- Na2HPO4 or Na4P2O7
Phosphoric acid reacts with metal fluorides dissolved in molten urea to yield monofluorphosphates.[5]
Properties
Monofluorophosphates are stable at room temperature, but will decompose when heated. For example, at 450 K silver monofluorophosphate gives off phosphoryl fluoride (POF3) as a gas leaving behind silver phosphate (Ag3PO4) and silver pyrophosphate (Ag4P2O7).[6]
In inorganic compounds the monofluorophosphate ion has an average P-O bond length of 1.51 Å. The P-F bond is longer, on average 1.58 Å. The O-P-F angle is 104.8°, smaller than the tetrahedral 109.47°. To compensate the O-P-O bond angle is 113.7° on average.[7]
Most commonly the monofluorophosphtae ion takes on point group 1, but a significant number have point group m. Only two are known with 3m and one with 3.[7]
When compared to sulfates, some are isotypical with the monofluorophosphates. Yet others have sulfates that take on a different form. But most know monofluorophosphates have no known equivalent sulfate.[7]
Compounds
| name | Formula | crystal form | Formula weight | density | ChemSpider | PubChem | CAS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fluorophosphoric acid | H2PO3F | 99.986 | 22687 | 24267 | 13537-32-1 | |||
| ammonium monofluorophosphate[8] | (NH4)2PO3F | orthorhombic a=6.29 Å, b=8.31 Å, c=12.70 Å, V=Å3 ß=99.6°, 4 per unit cell (Z)[9] | 134.05 | 1.633 | 8324505 | |||
| ammonium monofluorophosphate hydrate[10] | (NH4)2PO3F•H2O | monoclinic a=7.9481 Å, b=11.3472 Å, c=6.0425 Å, V=Å3 ß=117.55°, 4 per unit cell monoclinic a=6.3042, b=8.2942 c=12.760 β=98.415° Z=4 V=657.416[11] |
152.05 | 1.536 | ||||
| sodium monofluorophosphate | Na2PO3F | 22686 | 24266 | 10163-15-2 | ||||
| sodium hydrogen monofluorophosphate | NaHPO3F | 121.968 | 19860808 | 20859-36-3 | ||||
| sodium hydrogen monofluorophosphate dihydrate[12] | NaHPO3F.2H2O | monoclinic a=19.112Å, b=5.341Å, c=12.72Å, α=110.18°, V=1219.4. | 167.01 | 1.819 | ||||
| magnesium monofluorophosphate | MgPO3F | 122.28 | 23206079 | |||||
| diammonium manganese dimonofluorophosphate dihydrate[7] | (NH4)2Mg(PO3F)2•2H2O | monoclinic C2/m a=13.374 Å, b=5.3541 Å, c=7.385 Å, β=113.758° V=484.01 Z=2 | 292.37 | 2.006 | ||||
| potassium monofluorophosphate[8] | K2PO3F | orthorhombic a=7.554 Å, b=5.954 Å, c=10.171 Å, V=457Å3 Z=4 (at 20 °C) Z=4[13] | 176.17 | 2.57 | 20859-37-4 14306-73-1 | |||
| K2PO3F•KF[14] | ||||||||
| Potassium hydrogen monofluorophosphate | KHPO3F | monoclinic a=7.273; b=14.086; c=7.655 β=90.13 Z=8 V=784.233[15] | ||||||
| Tripotassium hydrogen monofluorophosphate | K3H(PO3F)2 | monoclinic a=7.973; b=11.635; c=9.668 β=113.52 Z=4 V=822.35[15] | ||||||
| Ammonium dipotassium hydrogen difluorophosphate[16] | NH4K2H(PO3F)2 | |||||||
| calcium monofluorophosphate dihydrate[17] | CaPO3F•2H2O | triclinic a=8.6497; b=6.4614; c=5.7353 α=119.003; β=110.853; γ=94.146 V=249.943 Z=2[11] | 2.313 | 8096036 | 9920401 | 37809-19-1 | ||
| calcium monofluorophosphate hemihydrate[17] | CaPO3F.1/2H2O | |||||||
| vanadium monofluorophosphate | VPO3F | 148.91 | 20452625 | |||||
| chromium(III) monofluorophosphate[7] | Cr2(PO3F)3•18.8H2OF | triclinic 11.594 b=15.292 c=15.360 α=83.804 β=84.203; γ=82.597 V=2674.1 Z=4 | 736.88 | 1.830 | ||||
| ammonium chromium(III) difluorophosphate hexahydrate[7] | NH4Cr(PO3F)2•6H2O | R3_m a=6.5491 c=25.438 Z=3 | 9.4489 | 1.972 | green | |||
| manganese(II) fluorophosphate dihydrate | MnPO3F•2H2O | triclinic Z = 2, a = 5.528, b = 5.636, c = 8.257 Å, α = 81.279, β = 75.156, γ = 71.722°[18] | 188.94 | |||||
| diammonium manganese monofluorophosphate[7] | (NH4)2Mn(PO3F)2•2H2O | monoclinic P21/n a=12.558 b=5.5456 c=7.422 β=99.918 Z=2 | 500.9 | 2.142 | pink | |||
| ammonium trimanganese dimonofluorophosphate difluorophosphate difluoride[19] | (NH4)Mn3(PO3F)2(PO2F2)F2 | monoclinic a=20.3151 b=7.6382 c=7.8312 β=103.589 V=1181.16 | 517.8 | 2.9116 | ||||
| diammonium cobalt dimonofluorophosphate dihydrate[7] | (NH4)2Co(PO3F)2•2H2O | monoclinic C2/m a=13.386 Å, b=5.3476 Å, c=7.390 Å, β=114.02° V=483.2 Z=2 | 326.99 | 2.247 | ||||
| ammonium tricobalt dimonofluorophosphate difluorophosphate difluoride[19] | (NH4)Co3(PO3F)2(PO2F2)F2 | monclinic a=19.9678 b=7.4883 c=7.5679 β= 102.676 V=1104.01 | 529.7 | 3.1871 | ||||
| Diammonium nickel dimonofluorophosphate hexahydrate[7] | (NH4)2Ni(PO3F)2•6H2O | monoclinic a=6.2700 b=12.2845 c=9.1894 β=106.033 Z=2 | 680.27 | 1.947 | blue Tutton | |||
| copper monofluorophosphate[20] | CuPO3F•5H2O | 251.59 | ||||||
| basic copper potassium monofluorophosphate[20] | Cu2K(OH)(PO3F)2•5H2O | monoclinic a=9.094 Å, b=6.333 Å, c=7.75 Å, ß=117.55°, 2 per unit cell. | natrochalcite | |||||
| diammonium diaquabis(monofluorophosphato) copper[21] | Cu(NH4)2(PO3F)2•2H2O | monoclinic a=13.454 Å, b=5.243 Å, c=7.518 Å, β=114.59° V=482.2 Z=2 | 331.6 | 2.28 | ||||
| basic tetraammonium dicopper dimonofluorophosphate[7] | NH4Cu2OH(PO3F)2•H2O | C2/m a=9.1012 b=6.4121 c=7.8506 β=116.277 Z=2 | 410.80 | 3.040 | light blue natrochalcite | |||
| zinc monofluorophosphate[22][7] | ZnPO3F•2.5H2O | triclinic a=7.6020 b=7.6490 c=9.4671 α = 88.633, β = 88.888, γ=87.182 V=549.58 Z=4 | 163.35 | 2.518 | 20846323 | 68705-59-9 | ||
| anhydrous diammonium zinc tetramonofluorophosphate[7] | (NH4)2Zn3(PO3F)4 | cubic a=11.4769 | ||||||
| diammonium zinc dimonofluorophosphate[7] | (NH4)2Zn(PO3F)2•0.2H2O | monoclinic C2/c a=18.936, b=7.6955 c=20.528, β=108.641 Z=?12 | 2834.4 | 2.117 | colourless | |||
| diammonium trizinc tetramonofluorophosphate[7] | (NH4)2Zn3(PO3F)4•H2O | cubic I4_3d a=11.3693 Z=4 | 1469.6 | 2.902 | colourless | |||
| rubidium monofluorophosphate[23] | Rb2PO3F | orthorhombic[24] a=7.8714 Å, b=6.1236 Å, c=10.5424 Å, V=508.15Å3 Z=4 (at 290K) Z=4 | 268.9 | 3.514 | ||||
| Rubidium hydrogen monofluorophosphate | RbHPO3F | monoclinic a=7.465, b=15.551, c=7.563, β=105.38, Z=8, V=846.533[15] | ||||||
| strontium monofluorophosphate | SrPO3F | monoclinic[25] | 185.59 | 18183579 | ||||
| strontium monofluorphosphate hydrate[26] | SrPO3F·H2O | 185.59 | ||||||
| silver monofluorophosphate[20] | Ag2PO3F | monoclinic a=9.245 Å, b=5.585 Å, c=14.784 Å, and β=90.178° Z=8[6] | 313.7 | 44135907 | ||||
| trisilver ammonium monofluorophosphate | NH4Ag3(PO3F)2 | monoclinic a=30.895, b=5.5976 c=9.7522, β=90.027 V=1686.6 Z=8[27] | 537.59 | 4.234 | ||||
| cadmium monofluorophosphate[7] | CdPO3F•2H2O | triclinic P1_ a=5.2678 b=6.6697 c=7.7037 α=65.506; β=85.919; γ=75.394 V=238.584 Z=2 | 246.40 | 3.430 | ||||
| tin monofluorophosphate | SnPO3F•2.5H2O | monoclinic | 216.68 | 44717639 | 52262-58-5 | |||
| caesium monofluorophosphate | Cs2PO3F[23] | orthorhombic a=8.308 Å, b=6.3812 Å, c=11.036 Å, V=585.1Å3 Z=4 at 240K | 363.8 | 4.129 | ||||
| caesium hydrogen monofluorophosphate | CsHPO3F | monoclinic a=14.478 Å, b=5.929 Å, c=5.413 Å, β=103.30°, V=452.2 Å3, Z = 4[28] | 231.89 | |||||
| tricaesium diammonium hydrogen monofluorophosphate | Cs3(NH4)2H3(PO3F)4 | monoclinic a=20.619 Å, b=12.076 Å, c=15.856 Å, β=102.58°, V=3853 Å3, Z=8[28] | 829.72 | |||||
| barium monofluorophosphate | BaPO3F | monoclinic a = 11.3105 Å, b = 8.6934 Å, c = 9.2231 Å, β = 127.819° Z=4 orthorhombic[29] |
235.299 | 20836124 | 15600-53-0[30] | |||
| Mercurous monofluorophosphate | Hg2PO3F | orthorhombic a=9.406 Å, b=12.145 Å, c=8.567 Å V=978.7 Z=8[31] | ||||||
| lead monofluorophosphate | PbPO3F | orthorhombic a=6.95 b=8.52 c=5.47[32] | 6.24 | |||||
| dilead monofluorophosphate dichloride hydrate[7] | Pb2(PO3F)Cl2•H2O | orthorhombic Pnma a=20.486 b=5.3967 c=6.9722 Z=4 V=770.8 | 601.27 | 5.181 | ||||
| ditheylammonium hydrogen monofluorophosphate[12] | [NH2(CH2CH3)2]HPO3F | orthorhombic a=12.892Å, b=9.530Å, c=13.555Å, α=90°, V=1665. | 173.12 | 1.381 | ||||
| tetramethylammonium monofluorophosphate[12] | [N(CH3)4]2PO3F | 246.26 | ||||||
| tetraethylammonium monofluorophosphate[12] | [N(CH2CH3)4]2PO3F | 358.47 | ||||||
| tetrabutylammonium monofluorophosphate[12] | [N(CH2CH2CH2CH3)4]2PO3F | 582.90 | ||||||
| piperazinium hydrogen monofluorophosphate[12] | [PipzH2]HPO3F | monoclinic a=6.020Å, b=13.012Å, c=7.285Å, α=95.09°, V=568.4 | 286.11 | 1.672 | ||||
| glutamine monofluorophosphate monohydrate | C5H12N2O3PFO3 | 246.131 | 19989732 | |||||
| glutamine monofluorophosphate disodium dichloride | C10H20Cl2FN4Na2O9P | 507.146 | 143826 | 164002 | ||||
| Anilinium Hydrogen Monofluorophosphate[33] | C6H8N+.HPO3F− | monoclinic a=9.418 Å b=14.31 Å c=6.303 Å β=92.45° V=859 Z=4 brown | 193.12 | 1.51 | ||||
| Tris(2-carbamoylguanidinium) hydrogen fluorophosphonate fluorophosphonate monohydrate[34] | 3C2H7N4O+·HFPO3−·FPO32−·H2O | triclinic a=6.7523, b = 8.2926, c = 9.7297, α= 100.630°,β=90.885°,γ=99.168, V = 528.05 | ||||||
| bis(2-carbamoylguanidinium) fluorophosphonate dihydrate[35] | 2C2H7N4O+·FPO32−·2H2O |
Organic
| name | Formula | Formula weight | ChemSpider | PubChem | CAS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimethyl fluorophosphate | (CH3)2PO2F | 128.039 | 72304 | 80052 | 5954-50-7 | ||
| Methyl ethyl fluorophosphate | (CH3)(CH3CH2)PO2F | ||||||
| 1-[Ethoxy(fluoro)phosphoryl]oxyethane[36] | (CH3CH2)2PO2F | 156.093 | 67752 | 358-74-7 | |||
| Isoflurophate | [(CH3)2CH]2PO2F | 184.147 | 5723 | 5936 | 55-91-4 | ||
| 1-[Fluoro(2-oxopropoxy)phosphoryl]oxypropan-2-one | 212.113 | 129718773 | |||||
| isobutyl methyl fluorophosphate[37] | 170.12 | 129684440 | |||||
| 1-[Fluoro(methoxy)phosphoryl]oxypentane | (CH3)(CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2)PO3F | 184.147 | 129761096 | ||||
| 1-[Fluoro(propoxy)phosphoryl]oxypropane | (CH3CH2CH2)2PO3F | 184.147 | 4954063 | 6451603 | 381-45-3 | ||
| O-isopropyl propyl fluorophosphonate | (CH3)2CH(CH3CH2CH2)PO3F | 184.147 | 88538036 | ||||
| O-1-methyl-butyl ethyl fluorophosphonate | 198.174 | 129761095 | |||||
| Dibutyl fluorophosphate | (CH3CH2CH2CH2)2PO3F | 212.201 | 11640560 | 13025172 | 674-48-6 | ||
| Di-sec-butyl fluorophosphate | [CH3CH2CH(CH3)]2PO3F | 212.201 | 92528 | 102452 | 625-17-2 | ||
| Di(1,3-dimethyl-n-butyl) fluorophosphate | [(CH3)2CHCH2CH(CH3)]2PO3F | 268.309 | 91838 | 101643 | 311-60-4 | ||
| 1-[fluoro(2-methylpentan-3-yloxy)phosphoryl]oxyoctane | 296.363 | 129760905 | |||||
| Methyl arachidonoyl fluorophosphonate | 400.471 | 11741711 | 9916415 | ||||
| 12-[fluoro(propan-2-yloxy)phosphoryl]oxydodec-1-ene | 308.374 | 129892247 | |||||
| bis(4-phenylbutyl) fluorophosphate | (C6H5CH2CH2CH2CH2)2PO3F | 364.397 | 162961 | 187452 | 85473-46-7 | ||
| 3'-Fluoro-3'-deoxythymidine-5'-fluorophosphate | 326.193 | 2339398 | 3081896 | 152829-59-9 | |||
| Cytidine 5'-fluorophosphate | 325.189 | 87861929 | 68521-86-8 | ||||
| Chlorofluoromethylideneamino-2-chloroethylfluorophosphate | ClFC-N-(ClCH2CH2PO3F | A-230 Novichok agent[38] | |||||
| Chlorofluoromethylideneamino-1-methyl-2-chloroethylfluorophosphate | ClFC-N-(ClCH2CH(CH3)PO3F | A-232 Novichok agent | |||||
| Chlorofluoromethylideneamino-1,2-dimethyl-2-chloroethylfluorophosphate | ClFC-N-(Cl(CH3)CHCH(CH3)PO3F | A-234 Novichok agent |
Uses
Zinc monofluorophosphate can be used as a corrosion inhibitor for steel when salt is present.[39]
Glutamine monofluorophosphate has been used as a fluoride-bearing medicine.
References
- ^ Cotton, F. Albert; Wilkinson, Geoffrey (1966). Advanced Inorganic Chemistry: A Comprehensive Text. John Wiley & Sons. p. 516.
- ^ Baynes, John W.; Dominiczak, Marek H. (2018). Medical Biochemistry E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 72. ISBN 9780702073007.
- ^ Zech, Ronald; Chemnitius, JörgM. (2002). "PON1 in Different Species". Paraoxonase (PON1) in Health and Disease. Springer US. pp. 137–163. doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-1027-7_7. ISBN 9781461353584.
- ^ Shaw, Cathy M.; James E. Shelby (1988). "Effect of Lead Compounds on the Properties of Stannous Fluorophosphate Glasses". Journal of the American Ceramic Society. 71 (5): C–252–C–253. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1988.tb05071.x. ISSN 0002-7820.
- ^ Schülke, U.; R. Kayser (1991). "Herstellung von Fluorophosphaten, Difluorophosphaten, Fluorophsophonaten und Fluorophosphiten in fluoridhaltigen Harnstoffschmelzen". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie (in German). 600 (1): 221–226. doi:10.1002/zaac.19916000130. ISSN 0044-2313.
- ^ a b Weil, Matthias; Michael Puchberger, Ekkehard Füglein, Enrique J. Baran, Julia Vannahme, Hans J. Jakobsen, Jørgen Skibsted (2007). "Single-Crystal Growth and Characterization of Disilver(I) Monofluorophosphate(V), Ag2PO3F: Crystal Structure, Thermal Behavior, Vibrational Spectroscopy, and Solid-State 19F, 31P, and 109Ag MAS NMR Spectroscopy". Inorganic Chemistry. 46 (3): 801–808. doi:10.1021/ic061765w. ISSN 0020-1669. PMID 17257023.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Weil, Matthias (7 January 2021). "Monofluorophosphates—New Examples and a Survey of the PO3F2− Anion". Chemistry. 3 (1): 45–73. doi:10.3390/chemistry3010005.
- ^ a b Bhattacharjee, Manish; Mihir K. Chaudhuri (1987). "Direct synthesis of ammonium monofluorophosphate monohydrate, [NH4]2[PO3F].H2O and potassium monofluorophosphate, K2[PO3F]". Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions (2): 477. doi:10.1039/DT9870000477. ISSN 0300-9246.
- ^ Krupková, Radmila; Jan Fábry, Ivana Císařová, Přemysl Vaněk (2002). "Bis(ammonium) fluorophosphate at room temperature". Acta Crystallographica Section C. 58 (5): i66–i68. doi:10.1107/S010827010200553X. ISSN 0108-2701. PMID 11983961.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Berndt, A. F.; J. M. Sylvester (1972). "The crystal structure of ammonium monofluorophosphate: (NH4)2PO3F.H2O" (PDF). Acta Crystallographica Section B. 28 (7): 2191–2193. doi:10.1107/S0567740872005771. ISSN 0567-7408.
- ^ a b Perloff, A. (1 July 1972). "The crystal structures of hydrated calcium and ammonium monofluorophosphates: CaPO3F.2H2O and (NH4)2 PO3F.H2O". Acta Crystallographica Section B. 28 (7): 2183–2191. doi:10.1107/S056774087200576X.
- ^ a b c d e f Prescott, Hillary Anne (2002-08-01). "The crystal structures and thermal behavior of hydrogen monofluorophosphates and basic monofluorophosphates with alkali metal and N-containing cations". Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftliche Fakultät I: 32. doi:10.18452/14706. Retrieved 1 November 2014.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Payen, Jean-Luc; Jean Durand, Louis Cot, Jean-Louis Galigne (1979). "Etude structurale du monofluorophosphate de potassium K2PO3F". Canadian Journal of Chemistry. 57 (8): 886–889. doi:10.1139/v79-146. ISSN 0008-4042.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Grimmer, Arnd-Rüdiger; Dirk Müller, Jochen Neels; Neels, Jochen (1985). "Solid-state high-resolution NMR K2PO3F·KF". Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 29 (1–2): 60. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(00)83295-9. ISSN 0022-1139.
- ^ a b c Prescott, Hillary A.; Troyanov, Sergej I.; Kemnitz, Erhard (1 January 2003). "The crystal structures of the potassium hydrogen monofluorophosphates, KHPO3F and K3[H(PO3F)2], and the α modification of RbHPO3F". Zeitschrift für Kristallographie - Crystalline Materials. 218 (9): 604. Bibcode:2003ZK....218..604P. doi:10.1524/zkri.218.9.604.20681. S2CID 100991538.
- ^ Fábry, Jan; Krupková, Radmila; Císařová, Ivana (24 January 2003). "Ammonium dipotassium hydrogen difluorophosphate at room temperature". Acta Crystallographica Section E. 59 (2): i14–i16. doi:10.1107/S160053680300117X.
- ^ a b Rowley, H. H.; John E. Stuckey (1956). "Preparation and Properties of Calcium Monofluorophosphate Dihydrate". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 78 (17): 4262–4263. doi:10.1021/ja01598a022. ISSN 0002-7863.
- ^ Weil, Matthias; Baran, Enrique J.; Kremer, Reinhard K.; Libowitzky, Eugen (February 2015). "Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Properties of Mn(PO3F)(H 2O)2". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie. 641 (2): 184–191. doi:10.1002/zaac.201400587.
- ^ a b Jiang, Jianhua; Zhu, Bei; Zhu, Tianyu; Yang, Haoming; Jin, Yong; Lü, Minfeng (2020). "Open-framework ammonium transition metal fluorophosphates with a Kagomé lattice network: synthesis, structure and magnetic properties". Dalton Transactions. 49 (3): 841–849. doi:10.1039/C9DT03370J. ISSN 1477-9226. PMID 31854410.
- ^ a b c Möwius, Frank; Burkhard Ziemer, Manfred Meisel, Herbert Grunze; Meisel, Manfred; Grunze, Herbert (1985). "On a new type of copper monofluorophosphate". Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 29 (1–2): 68. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(00)83303-5. ISSN 0022-1139.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Berraho, M.; A. Vegas, M. Martínez-Ripoll, M. Rafiq (1994). "A copper monofluorophosphate, Cu(H2O)2(NH4)2(PO3F)2". Acta Crystallographica Section C. 50 (5): 666–668. doi:10.1107/S0108270193010789. ISSN 0108-2701.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Möwius, F.; M. Meisel, H. Kirk, W. Unger, D. Seepe, W. Metzner (1990). "Fluorophosphate—eine neue Wirkstoffgruppe für Holzschutzmittel". Holz Als Roh- und Werkstoff (in German). 48 (9): 345–350. doi:10.1007/BF02639896. ISSN 0018-3768.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Fábry, Jan; Michal Dušek, Karla Fejfarová, Radmila Krupková, Přemysl Vaněk, Ivana Císařová (2006). "Dirubidium fluorotrioxophosphate, Rb2PO3F, at 290 and 130 K, and dicaesium fluorotrioxophosphate, Cs2PO3F, at 240 and 100 K". Acta Crystallographica Section C. 62 (6): i49–i52. doi:10.1107/s0108270106016350. ISSN 0108-2701. PMID 16763294.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "List of Substances". AtomWork. Retrieved 4 November 2014.
- ^ Rafiq, M.; Durand J.; Cot L (1979). "étude cristallographique des phosphites des métaux alcalinoterreux". Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, Série C. 288 (15): 411–413.
- ^ Menz, D.-H.; L. Kolditz, K. Heide, Ch. Kunert, Ch. Mensing (1986). "Zur Thermischen Zersetzung von SrPO3F·H2O". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie. 540 (9–10): 191–197. doi:10.1002/zaac.19865400920. ISSN 0044-2313.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Weil, Matthias (14 April 2007). "NH4Ag3(PO3F)2, a layered monofluorophosphate(V) with seven different Ag sites". Acta Crystallographica Section C. 63 (5): i31–i33. doi:10.1107/S0108270107008967. PMID 17478892.
- ^ a b Kemnitz, Erhard; Prescott, Hillary A.; Troyanov, Sergey I. (1 January 2000). "The crystal structures of two hydrogen monofluorophosphates: CsHPO3F and Cs3(NH4)2(HPO3F)3(PO3F)". Zeitschrift für Kristallographie - Crystalline Materials. 215 (4): 240. Bibcode:2000ZK....215..240K. doi:10.1524/zkri.2000.215.4.240. S2CID 91421180.
- ^ Stöger, Berthold; Matthias Weil, Jørgen Skibsted; Skibsted, Jørgen (2013). "The crystal structure of BaPO3F revisited – a combined X-ray diffraction and solid-state 19F, 31P MAS NMR study". Dalton Transactions. 42 (32): 11672–82. doi:10.1039/C3DT50373A. ISSN 1477-9226. PMID 23838743.
- ^ "15600-53-0 - QNHNZAMKMLIQRR-UHFFFAOYSA-L - Barium fluorophosphate". ChemIDplus. Retrieved 4 November 2014.
- ^ Weil, Matthias; Puchberger, Michael; Baran, Enrique J. (December 2004). "Preparation and Characterization of Dimercury(I) Monofluorophosphate(V), Hg2PO3F: Crystal Structure, Thermal Behavior, Vibrational Spectra, and Solid-State 31P and 19F NMR Spectra". Inorganic Chemistry. 43 (26): 8330–8335. doi:10.1021/ic048741e. PMID 15606179.
- ^ Walford, L. K. (1967). "Single-crystal and powder data for lead fluorophosphate". Acta Crystallographica. 22 (2): 324. doi:10.1107/S0365110X67000593. ISSN 0365-110X.
- ^ Khaoulani Idrissi, A.; Rafiq, M.; Gougeon, P.; Guerin, R. (15 July 1995). "Anilinium Hydrogen Monofluorophosphate, C6H8N+.HPO3F−". Acta Crystallographica Section C. 51 (7): 1359–1361. doi:10.1107/S010827019401214X.
- ^ Fábry, Jan; Michaela Fridrichová, Michal Dušek, Karla Fejfarová, Radmila Krupková (2011). "Tris(2-carbamoylguanidinium) hydrogen fluorophosphonate fluorophosphonate monohydrate". Acta Crystallographica Section E. 68 (1): o47–o48. doi:10.1107/S1600536811051683. ISSN 1600-5368. PMC 3254407. PMID 22259550.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Fábry, Jan; Michaela Fridrichová, Michal Dušek, Karla Fejfarová, Radmila Krupková (2012). "Two polymorphs of bis(2-carbamoylguanidinium) fluorophosphonate dihydrate". Acta Crystallographica Section C. 68 (2): o71–o75. doi:10.1107/S0108270111053133. ISSN 0108-2701. PMID 22307257.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Zavorin, S. I.; Lermontov, S. A.; Martynov, I. V. (May 1988). "Fluorination of some phosphoric acid derivatives". Bulletin of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR Division of Chemical Science. 37 (5): 1033–1035. doi:10.1007/BF00957090. S2CID 98659309.
- ^ Ordentlich, Arie; Barak, Ruth; Barak, Dov; Fischer, Meir; Benschop, HendrikP.; De Jong, LeoP.A.; Segall, Yoffi; Velan, Baruch; Shafferman, Avigdor (1998). "ESMS as a Unique Tool for the Molecular Monitoring of Reactions between HuAChE and Various OP-Agents". Structure and Function of Cholinesterases and Related Proteins. Springer US. p. 249. doi:10.1007/978-1-4899-1540-5_74. ISBN 9781489915429.
- ^ Halámek, Emil & Kobliha, Zbynek. (2011). Potential Chemical Warfare Agents. Chemicke Listy. 105. 323-333.
- ^ Duprat, M.; A. Bonnel, F. Dabosi, J. Durand, L. Cot (1983). "Les monofluorophosphates de zinc et de potassium en tant qu'inhibiteurs de la corrosion d'un acier au carbone en solution de NaCl à 3%". Journal of Applied Electrochemistry. 13 (3): 317–323. doi:10.1007/BF00941603. ISSN 0021-891X. S2CID 95845823.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)