Aluminized steel
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2011) |
Aluminized steel is steel that has been plated with aluminium or aluminium-silicon alloy, in a process analogous to hot-dip galvanizing. The steel workpiece is immersed in molten aluminum to produce a tight metallic bond between the steel and coating. The product has a unique combination of properties possessed by neither steel alone nor aluminium alone. Aluminized steel is more resistant to corrosion than bare steel[1] while retaining properties of steel, at temperature lower than the melting point of aluminum, 800 °C (1,470 °F). Common applications include heat exchangers in residential furnaces, commercial rooftop HVAC units, automotive mufflers, ovens, kitchen ranges, water heaters, fireplaces, barbecue burners, and baking pans. Aluminized steel transfers heat more effectively than bare steel. It often serves where galvanized steel might have been used historically, without galvanized steel's drawbacks.
Characteristics vary depending on the aluminum alloy used.
Types
- Type 1
- Hot-dip coated with a thin layer of aluminium-silicon alloy. 5% to 11% added silicon promotes better adherence. It is intended principally for heat resisting applications and also for uses where corrosion resistance and heat are required. Possible end uses are mufflers, furnaces, ovens, ranges, heaters, water heaters, fireplaces, and baking pans. Aluminized steel can withstand 550 °C (1,022 °F) with almost no change in the base material. But due to silicon content it develops black spot. Aluminized steel has slowly started to convert bakery trays which were previously made by galvanized or galvalume steel as it does not contain lead which is poisonous. Type 1 is also commonly found in industrial products.
- Type 2
- Hot-dip coated with commercially pure aluminum. It is intended principally for applications requiring atmospheric corrosion resistance. Type 2 may ultimately be manufactured into corrugated roofing and siding, grain bins, drying ovens, and air-conditioner condenser housings.
Properties
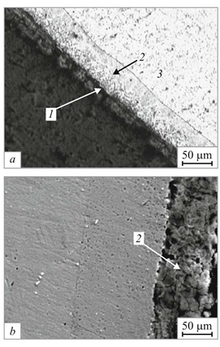

The basic structure of aluminized steel is a thin aluminium oxide layer outside, then an intermetallic layer that is a mix of aluminium, silicon, and steel, and finally a steel core.[2]
Both Type 1 and Type 2 show excellent high reflectivity characteristics. At temperatures up to 842 °C (1,548 °F), aluminized steel reflects up to 80% of heat projected onto it.[3] Aluminized steel has the ability to maintain its strength at temperatures up to 677 °C (1,251 °F). Although stainless steel is the stronger of the two, aluminized steel has a greater electrostatic surface, and can therefore reflect heat better.
Aluminized steel is highly resistant to corrosion because of the thin layers of aluminium and silicon, which keep the underlying steel from oxidizing. These thin layers also keep pit corrosion from occurring, especially during exposure to salts that affect most other metals. However, despite the good corrosion resistance of aluminized steel, if the aluminium layer is disrupted and the steel is exposed, then the steel may oxidize and corrosion may occur.
Consumption
In North America nearly 700,000 tons of aluminized steel are consumed annually.[4] Some of the common products made from aluminized steel include water heaters, ranges, furnaces, space heaters and grills.
Processing
Aluminized steel can be made using a variety of processes, cladding, hot dipping, galvanic coating, metallizing, and calorizing, but the most effective process is hot dipping. The process of hot dipping starts by cleaning the steel, then placing the steel in a bath of Al-11%Si at a temperature of 988K and shaken, then pulled out and air dried.[5] The aluminium diffuses into the steel, creating an intermetallic layer above the steel base layer, but below the outside aluminum coating. The aluminium coating is oxidized to help protect the inner steel from corrosion and further aluminium diffusion.[6] The silicon is added to the aluminium bath to create a thinner layer of aluminium on the steel. The hot dipping process is cheaper and more effective to produce aluminized steel than any other process.[7]
Uses

Aluminized steel was developed for providing more structural durability and a high yield strength in highly corrosive environments. It maintains the strength of high-alloy steel, but is cheaper to produce than high-alloy steels and thus is a preferred material for manufacturing automobile and motorcycle exhaust gas systems.[7]
Al-Si coatings are used to protect boron steel when hot pressing.
See also
References
- ^ ""Aluminized steel Offers Attractive Physical Characteristics For Use In Industrial Duct Construction". Sheet Metal and Air Conditioning Contractors' National Association. Retrieved 26 Feb 2011". Archived from the original on 2011-02-20. Retrieved 2011-02-26.
- ^ Kee-Hyun, Kim. Van-Daele, Benny. Van-Tendeloo, Gusfaaf. and Jong-Kyu, Yoon. (2006). "Observations of Intermetallic Compound Formation of Hot Dip Aluminized steel". Materials Science Forum, 519-21(2), 1871-75.
- ^ Atlas Steel - Aluminized steel
- ^ "Block Steel Aluminized Steel Specialists". Archived from the original on 2010-09-30. Retrieved 2011-11-29.
- ^ Rajendran, R. Venkataswamy, S. Jaikrishna, U. Gowrishankar, N. and Rajadurai, A. (2006). "Effect of Process Parameters in Hot Dip Aluminizing of Medium Carbon Steel".
- ^ Deqing, Wang. and Ziyuan, Shi. (2003) "Formation of Al2O3 Layer on Steel". Journal of Materials Science Letters, 22(14), 1003-1006.
- ^ a b Wang, Chaur. Jeng. Badaruddin, Mohd.. (2010) "The dependence of high temperature resistance of aluminized steel exposed to water-vapour oxidation". Surface and Coatings Technology, 205(5), 1200-1205.
