Sodium sorbate
Appearance
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
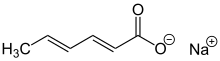
Sodium (2E,4E)-hexa-2,4-dienoate | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.927 | ||
| E number | E201 (preservatives) | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H7NaO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 134.10835 g/mol | ||
| Odor | hydrocarbon-like | ||
| Boiling point | 233 °C (451 °F; 506 K)[1] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Sodium sorbate is the sodium salt of sorbic acid. It is an unstable white solid. Unlike other sorbic acid salts such as potassium sorbate (E202) and calcium sorbate (E203), the use of sodium sorbate as a food additive is not allowed in the EU due to potential genotoxic effects.[2][3]
Its E-number is E201.
References
- ^ Datenbankeintrag bei Chemspider
- ^ EFSA Journal 2015
- ^ Erich Lück, Martin Jager, Nico Raczek (2000). "Sorbic Acid". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a24_507. ISBN 3527306730.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)


