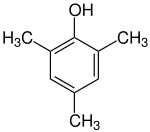
Mesitol
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,4,6-Trimethylphenol | |
| Other names
Hydroxymesitylene; Mesityl alcohol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.655 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H12O | |
| Molar mass | 136.194 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 70–72 °C (158–162 °F; 343–345 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 220 °C (428 °F; 493 K)[1] |
| 1.01 g/l | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H314, H411 | |
| P260, P264, P273, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P391, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Mesitol (2,4,6-trimethylphenol) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)3C6H2OH. It is one of several isomers of trimethylphenol. The name and structure of mesitol derives from the combination of mesitylene and phenol.
Synthesis
[edit]Mesitol is the main product from the methylation of phenol with methanol in the presence of a solid acid.[2]
It can also be obtained by reaction of mesitylene with peroxymonophosphoric acid:[3]
An alternative route involves palladium-catalyzed reaction of bromomesitylene with potassium hydroxide.[4]
References
[edit]- ^ a b "2,4,6-Trimethylphenol". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ^ Fiege, Helmut; Voges, Heinz-Werner; Hamamoto, Toshikazu; Umemura, Sumio; Iwata, Tadao; Miki, Hisaya; Fujita, Yasuhiro; Buysch, Hans-Josef; Garbe, Dorothea; Paulus, Wilfried (2000). "Phenol Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_313. ISBN 3527306730.
- ^ Ogata, Yoshiro; Sawaki, Yasuhiko; Tomizawa, Kohtaro; Ohno, Takashi (1981). "Aromatic hydroxylation with peroxymonophosphoric acid". Tetrahedron. 37 (8): 1485. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)92087-3.
- ^ Anderson, Kevin W.; Ikawa, Takashi; Tundel, Rachel E.; Buchwald, Stephen L. (2006). "The Selective Reaction of Aryl Halides with KOH: Synthesis of Phenols, Aromatic Ethers, and Benzofurans". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 128 (33): 10694–10695. doi:10.1021/ja0639719. PMID 16910660.

