Α-Eucaine
Appearance
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Alpha-Eucaine |
| Other names | α-Eucaine; Eucaine A |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
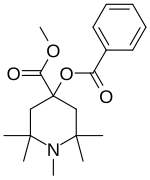
| Formula | C19H27NO4 |
| Molar mass | 333.428 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
alpha-Eucaine is a drug that was previously used as a local anesthetic.[1] It was designed as an analog of cocaine and was one of the first synthetic chemical compounds to find general use as an anesthetic.[2]
See also
- Eucaine, a related local anesthetic
References
- ^ Walter Sneader (31 October 2005). Drug Discovery: A History. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 127–9. ISBN 978-0-470-01552-0.
- ^ R. H. F. Manske (12 May 2014). The Alkaloids: Chemistry and Physiology. Elsevier. pp. 213–4. ISBN 978-1-4832-2192-2.
