Raymond–Céstan syndrome
| Raymond–Céstan syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | upper dorsal pontine syndrome, |
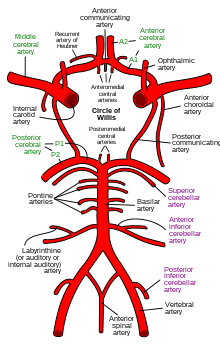 | |
| Basillar artery runs down the middle(in above image) and blockage is cause of this condition | |
Raymond-Céstan syndrome is caused by blockage of the long circumferential branches of the basilar artery.[1] It was described by Fulgence Raymond and Étienne Jacques Marie Raymond Céstan.[2] Along with other related syndromes such as Millard-Gubler syndrome, Foville's syndrome, and Weber's syndrome, the description was instrumental in establishing important principles in brain-stem localization.[3]
Presentation
- Ipsilateral ataxia and coarse intention tremor (damage to superior and middle cerebellar peduncle)
- Ipsilateral paralysis of muscles of mastication and sensory loss in face (damage to sensory and motor nuclei and tracts of CN V)
- Contralateral loss of sensory modalities in the body (damage to spinothalamic tract and medial lemniscus)
- Contralateral hemiparesis of face and body (damage to corticospinal tract) may occur with ventral extension of lesion
- Horizontal gaze palsy may occur (as in lower dorsal pontine syndrome)
Diagnosis
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (October 2017) |
Treatment
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (October 2017) |
References
- ^ http://www.clineu-journal.com/article/S0303-8467(07)00181-3/abstract
- ^ "Céstan-Chenais syndrome".
- ^
Silverman, IE; Liu, GT; Volpe, NJ; Galetta, SL (June 1995). "The crossed paralyses. The original brain-stem syndromes of Millard-Gubler, Foville, Weber, and Raymond-Cestan". Archives of Neurology. 52 (6): 635–8. doi:10.1001/archneur.1995.00540300117021. PMID 7763214.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)
Further reading
- Kim, JS; Lee, JH; Im, JH; Lee, MC (Jun 1995). "Syndromes of pontine base infarction. A clinical-radiological correlation study". Stroke: A Journal of Cerebral Circulation. 26 (6): 950–5. doi:10.1161/01.STR.26.6.950. PMID 7762044.
- Krasnianski, M; Neudecker, S; Zierz, S (Aug 2004). "[Classical crossed pontine syndromes]". Fortschritte der Neurologie · Psychiatrie (in German). 72 (8): 460–8. doi:10.1055/s-2004-818392. PMID 15305240.
