Trihydroxybenzenes
Appearance
The trihydroxybenzenes (or benzenetriols) are organic compounds with the formula C6H3(OH)3. Also classified as polyphenols, they feature three hydroxyl groups substituted onto a benzene ring. They are white solids with modest solubility in water.[1]
Pyrogallol Hydroxyquinol Phloroglucinol Benzene-1,2,3-triol Benzene-1,2,4-triol Benzene-1,3,5-triol 
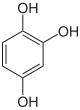

The enzyme pyrogallol hydroxytransferase uses benzene-1,2,3,5-tetrol and benzene-1,2,3-triol (pyrogallol), whereas its two products are benzene-1,3,5-triol (phloroglucinol) and benzene-1,2,3,5-tetrol. This enzyme can be found in Pelobacter acidigallici.[2][3]
References
- ^ "Phenol Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. 2002. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_313. ISBN 978-3527306732.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ "P 80564 Pyrogallol hydroxytransferase small subunit". UniProtKB. Uniprot.
- ^ Schink, B.; Pfennig, M. (December 1982). "Fermentation of trihydroxybenzenes by Pelobacter acidigallici gen. nov. sp. nov., a new strictly anaerobic, non-sporeforming bacterium". Archives of Microbiology. 133 (3): 195–201. doi:10.1007/BF00415000.
See also



