Archaeopriapulida
Appearance
| Archaeopriapulida Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
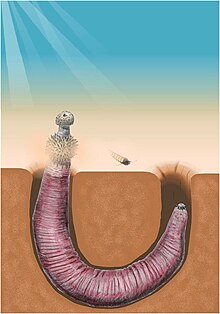
| |
| Reconstruction of the celebrated archaeopriapulid Ottoia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Stem group: | Priapulida (?) |
| Class: | †Archaeopriapulida |
Archaeopriapulida is a group of priapulid-like worms known from Cambrian lagerstätte.[3] The group is closely related to, and very similar to, the modern Priapulids.[4] It is unclear whether it is mono- or polyphyletic.[5] Despite a remarkable morphological similarity to their modern cousins,[6] they fall outside of the priapulid crown group, which is not unambiguously represented in the fossil record until the Carboniferous.[7] They are probably closely related or paraphyletic to the palaeoscolecids; the relationship between these basal worms is somewhat unresolved.[5]
Species
- Genus Acosmia maotiania Chen & Zhoi 1997 (Chengjiang deposits)
- Acosmia maotiania Chen & Zhoi 1997
- Genus Archotuba Hou et al. 1999 (possibly a Cnidarian) (Chengjiang deposits)[8]
- Archotuba conoidalis Hou et al. 1999
- Genus Baltiscalida Slater et al. 2017
- Baltiscalida njorda Slater et al. 2017
- Genus Eopriapulites Liu & al 2014[9]
- Eopriapulites sphinx Liu & al 2014
- Genus Eximipriapulus Ma et al. 2014 (Chengjiang deposits) [10]
- Eximipriapulus globocaudatus Ma et al. 2014
- Genus Gangtoucunia Luo & Hu 1999 (Chengjiang deposits)
- Gangtoucunia aspera Luo & Hu 1999 (May not be a priapulid)[11]
- Genus Lagenula Luo & Hu 1999 nomen dubium (Chengjiang deposits)[6]
- Lagenula striolata Luo & Hu 1999 nomen dubium
- Genus Laojieella Han et al. 2006 (Chengjiang deposits)[12]
- Laojieella thecata Han et al. 2006
- Genus Lecythioscopa Conway Morris 1977 (Burgess Shale)
- Lecythioscopa simplex (Walcott 1931) Conway Morris 1977 [Canadia simplex Walcott 1931]
- Genus Oligonodus Luo & Hu 1999 nomen dubium (Chengjiang deposits)[6]
- Oligonodus specialis Luo & Hu 1999 nomen dubium
- Genus Omnidens Hou & al 2006 (Chengjiang deposits)
- Omnidens amplus Hou & al 2006
- Genus Sandaokania Luo & Hu 1999 nomen dubium (Chengjiang deposits)[6]
- Sandaokania latinodosa Luo & Hu 1999 nomen dubium
- Genus Singuuriqia Peel 2017 (Sirius Passet)[13]
- Singuuriqia simoni Peel 2017
- Genus Sullulika Peel & Willman, 2018[14]
- Sullulika broenlundi Peel & Willman, 2018
- Genus Xishania Hong 1981
- Xishania fusiformis Hong 1981
- Xishania jiangxiensis Hong 1988
- Genus Paratubiluchus Han, Shu, Zhang et Liu, 2004 (Chengjiang deposits)
- Paratubiluchus bicaudatus Han, Shu, Zhang et Liu, 2004
- Genus Xiaoheiqingella Hu 2002
- Xiaoheiqingella peculiaris Hu 2002 [Yunnanpriapulus halteroformis Huang et al 2004[15]][16] (Chengjiang deposits)
- Genus Priapulites Schram 1973 (Mazon Creek)
- Priapulites konecniorum Schram 1973
- Family Palaeopriapulitidae Hou et al. 1999
- Genus Sicyophorus Luo & Hu 1999 (Chengjiang deposits)[6]
- Sicyophorus rara Luo & Hu 1999
- Sicyophorus sp.[17]
- Genus Paraselkirkia Luo & Hu 1999[18]
- Paraselkirkia sinica (Luo & Hu 1999) Luo & Hu 1999
- Genus Sicyophorus Luo & Hu 1999 (Chengjiang deposits)[6]
- Family Selkirkiidae Conway Morris 1977 (stem Palaeoscolecida)[19]
- Genus Selkirkia Walcott 1911
- Selkirkia elongata Luo & Hu 1999 (Chengjiang deposits)
- Selkirkia columbia Walcott 1911 (Burgess Shale)
- Selkirkia pennsylvanica Resser & Howell 1938
- Selkirkia spencei Resser 1939
- Selkirkia willoughbyi Conway Morris & Robison 1986
- Genus Selkirkia Walcott 1911
- Order Ancalagonida Adrianov & Malakhov 1995 (stem Scalidophora)[19]
- Family Ancalagonidae Conway Morris 1977
- Genus Ancalagon (Walcott 1911) Conway Morris 1977 (Burgess Shale)
- Ancalagon minor (Walcott 1911) Conway Morris 1977
- Genus Ancalagon (Walcott 1911) Conway Morris 1977 (Burgess Shale)
- Family Fieldiidae Conway Morris 1977
- Genus Fieldia Walcott 1912 (Burgess Shale)
- Fieldia lanceolata Walcott 1912
- Genus Fieldia Walcott 1912 (Burgess Shale)
- Genus Scolecofurca Conway Morris 1977 (Burgess Shale)
- Scolecofurca rara Conway Morris 1977
- Family Ottoiidae Walcott 1911
- Genus Ottoia Walcott 1911
- Ottoia cylindrica (Sun & Hou 1987)
- Ottoia guizhouenis Yang, Zhao & Zhang 2016
- Ottoia prolifica Walcott 1911 (Burgess Shale)
- Ottoia tenuis Walcott 1911
- Ottoia tricuspida Smith, Harvey & Butterfield 2015
- Genus Ottoia Walcott 1911
- Family Corynetidae Huang, Vannier & Chen 2004
- Genus Corynetis Luo & Hu 1999
- Corynetis brevis Luo & Hu 1999 [Anningvermis multispinosus Huang et al 2004[6]) (Chengjiang deposits)[10]
- Corynetis fortis Hu et al. 2012 [20] (Chengjiang deposits)
- Corynetis pusillus (Klug 1842)
- Genus Corynetis Luo & Hu 1999
- Family Miskoiidae Walcott 1911
- Genus Louisella Conway Morris 1977 (Burgess Shale)
- Louisella pedunculata (Walcott 1911) Conway Morris 1977
- Genus Miskoia Walcott 1911
- Miskoia placida Walcott 1931
- Miskoia preciosa Walcott 1911
- Genus Louisella Conway Morris 1977 (Burgess Shale)
- Family Ancalagonidae Conway Morris 1977
References
- ^ Smith, M. R.; Harvey, T. H. P.; Butterfield, N. J. (2015). "The macro- and microfossil record of the Cambrian priapulid Ottoia" (PDF). Palaeontology. 58 (4): 705–721. doi:10.1111/pala.12168.
- ^ Supplementary information from Smith, M.R.; Harvey, T.H.P.; Butterfield, N.J. (2015). "The macro- and microfossil record of the Cambrian priapulid Ottoia" (PDF). Palaeontology. 58 (4): 705–721. doi:10.1111/pala.12168.
- ^ Conway Morris, S. (1979). "The Burgess Shale (Middle Cambrian) Fauna". Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics. 10: 327–349. doi:10.1146/annurev.es.10.110179.001551.
- ^ Por, F. D. (1983). "Class Seticoronaria and Phylogeny of the Phylum Priapulida". Zoologica Scripta. 12 (4): 267–272. doi:10.1111/j.1463-6409.1983.tb00510.x.
- ^ a b Wills, M. A. (1 April 1998). "Cambrian and Recent Disparity: the Picture from Priapulids". Paleobiology. 24 (2): 155–286. JSTOR 2401237.
- ^ a b c d e f Huang, D.-Y.; Vannier, J.; Chen, J.-Y. (2004). "Anatomy and lifestyles of Early Cambrian priapulid worms exemplified by Corynetis and Anningvermis from the Maotianshan Shale (SW China)". Lethaia. 37: 21–33. doi:10.1080/00241160410005088.
- ^ Budd, G. E.; Jensen, S. (2000). "A critical reappraisal of the fossil record of the bilaterian phyla". Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society. 75 (2): 253–95. doi:10.1111/j.1469-185X.1999.tb00046.x. PMID 10881389.
- ^ Schmidt-Rhaesa, Andreas (2012-12-21). Nematomorpha, Priapulida, Kinorhyncha, Loricifera. ISBN 9783110272536.
- ^ Liu, Y.; Xiao, S.; Shao, T.; Broce, J.; Zhang, H. (2014). "The oldest known priapulid-like scalidophoran animal and its implications for the early evolution of cycloneuralians and ecdysozoans". Evolution & Development. 16 (3): 155–65. doi:10.1111/ede.12076. PMID 24754444.
- ^ a b Ma, X.; Aldridge, R. J.; Siveter, D. J.; Siveter, D. J.; Hou, X.; Edgecombe, G. D. (2014). "A New Exceptionally Preserved Cambrian Priapulid from the Chengjiang Lagerstätte". Journal of Paleontology. 88 (2): 371. doi:10.1666/13-082.
- ^ Hu, S.; Zhu, M.; Steiner, M.; Luo, H.; Zhao, F.; Liu, Q. (2010). "Biodiversity and taphonomy of the Early Cambrian Guanshan biota, eastern Yunnan". Science China Earth Sciences. 53 (12): 1765. doi:10.1007/s11430-010-4086-9.
- ^ Han, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shu, D. (2006). "A new theca-bearing Early Cambrian worm from the Chengjiang Fossil Lagerstätte, China". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. 30: 1–10. doi:10.1080/03115510608619340.
- ^ Peel, John S. (2017). "Feeding behaviour of a new worm (Priapulida) from the Sirius Passet Lagerstätte (Cambrian Series 2, Stage 3) of North Greenland (Laurentia)". Palaeontology. 60 (6): 795–805. doi:10.1111/pala.12316.
- ^ Peel, John S; Willman, Sebastian (2018). "The Buen Formation (Cambrian Series 2) biota of North Greenland". Papers in Palaeontology. 4 (3): 381–432. doi:10.1002/spp2.1112.
- ^ Huang, D.; Vannier, J.; Chen, J. (2004). "Recent Priapulidae and their Early Cambrian ancestors: Comparisons and evolutionary significance". Geobios. 37 (2): 217. doi:10.1016/j.geobios.2003.04.004.
- ^ Han, J.; Shu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J. (2004). "The earliest-known ancestors of Recent Priapulomorpha from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang Lagerstätte". Chinese Science Bulletin. 49 (17): 1860. doi:10.1007/BF03183414.
- ^ Zeng, H.; Zhao, F.; Yin, Z.; Li, G.; Zhu, M. (2014). "A Chengjiang-type fossil assemblage from the Hongjingshao Formation (Cambrian Stage 3) at Chenggong, Kunming, Yunnan". Chinese Science Bulletin. 59 (25): 3169. doi:10.1007/s11434-014-0419-y.
- ^ (Chengjiang deposits)Han, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Shu, D. (2007). "Evidence of Priapulid Scavenging from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang Deposits, Southern China". PALAIOS. 22 (6): 691–694. doi:10.2110/palo.2006.p06-117r. ISSN 0883-1351.[permanent dead link]
- ^ a b Haaramo, Mikko (2003). "Scalidophora – †palaeoscolecids, priapulids, mud dragons and brush heads". Mikko's Phylogeny Archive. Retrieved May 14, 2019.
- ^ Hu, S.; Steiner, M.; Zhu, M.; Luo, H.; Forchielli, A.; Keupp, H.; Zhao, F.; Liu, Q. (2012). "A new priapulid assemblage from the early Cambrian Guanshan fossil Lagerstätte of SW China". Bulletin of Geosciences: 93–106. doi:10.3140/bull.geosci.1238.
