M1841 6-pounder field gun
| M1841 6-pounder field gun | |
|---|---|
 M1841 6-pounder field gun at Antietam National Battlefield | |
| Type | Smoothbore cannon |
| Place of origin | United States |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1841–1868 |
| Used by | |
| Wars | Mexican–American War American Civil War |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Cyrus Alger & Co. N. P. Ames |
| Produced | 1841 |
| No. built | over 854 |
| Variants | 1835, 1838, 1840 |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 880 lb (399.2 kg) |
| Length | 5.0 ft (1.52 m) |
| Crew | 9 |
| Shell weight | 6.1 lb (2.8 kg) shot 1.25 lb (0.6 kg) charge |
| Caliber | 3.67 in (93 mm) |
| Barrels | 1 |
| Action | Muzzle loading |
| Carriage | 900 lb (408.2 kg) |
| Rate of fire | 2 rounds/minute |
| Muzzle velocity | 1,439 ft/s (439 m/s) |
| Effective firing range | 1,523 yd (1,393 m) |
The M1841 6-pounder field gun was a bronze smoothbore muzzle-loading cannon that was adopted by the United States Army in 1841 and used from the Mexican–American War to the American Civil War. It fired a 6.1 lb (2.8 kg) round shot up to a distance of 1,523 yd (1,393 m) at 5° elevation. It could also fire canister shot and spherical case shot. The cannon proved very effective when employed by light artillery units during the Mexican–American War. The cannon was used during the early years of the American Civil War, but it was soon outclassed by newer field guns such as the 12-pounder Napoleon. In the US Army, the 6-pounders were replaced as soon as more modern weapons became available and none were manufactured after 1862. However, the Confederate States Army continued to use the cannon for a longer period because the lesser industrial capacity of the South could not produce newer guns as fast as the North.
Background
"Iron Age"
By the early 1800s gun-founders knew that two metals were suitable for the manufacture of cannon, iron and bronze. Bronze, an alloy made up of about 90% copper and 10% tin, was strong enough to resist the explosion of gunpowder without bursting the cannon. The guns were often referred to as brass cannons when in fact their composition was of bronze. The weakness of bronze guns was that, if fired too rapidly, they overheated and warped. Iron cannons were much cheaper to manufacture and they did not warp from overheating. However, cast iron was more brittle than bronze. Iron cannons were heavier that bronze guns; this was not a problem with large caliber weapons aboard ships or in fortresses, but field artillery needed to be lighter and more mobile.[1]
Before a cannon was accepted into service, it was subjected to proof testing in order to determine if the piece met the specifications and was safe to fire. First, the gun was weighed and measured. Second, the gun was fired; if it burst, then the entire batch was given extra scrutiny.[2] Typically, a proofing charge used approximately twice the weight of gunpowder as a normal firing charge.[2] Third, the inside of the bore was probed with a special instrument to make sure there were no cracks or gaps. Fourth, the vent was stopped up and water was forced into the bore; if water leaked out the cannon was rejected. Fifth, a mirror was inserted into the bore for a final inspection.[3]
From 1820 to 1840, American cannon founders made cast iron 6-pounders that were less reliable than guns used in the War of 1812.[4] In 1824, the Fort Pitt Foundry delivered 74 cast iron 6-pounder guns of an order of 100.[5] A second order of 100 cast iron 6-pounders was delivered in 1828–1830 and at least 10 were rejected. Finally, 113 cast iron 6-pounders were manufactured in 1836–1838 and 22 were rejected. No more orders were placed with the Fort Pitt Foundry. In 1833, the Columbia Foundry produced two cast iron 6-pounders of which one burst during proof. They delivered 43 cast iron 6-pounders in 1834–1836 but these were the last ones produced by the Columbia Foundry.[6] In 1840, an exasperated Secretary of War Joel Roberts Poinsett wrote, "...if guns sometimes fail, it is not because the gun is of iron, but because the founder is not perfect in his art. At present, he makes a good gun by accident, whereas it is by accident only that he should make a bad one."[7] Soon afterward, the problem was finally discovered. During this period, American cannon founders switched from cold blast to hot blast cast iron for reasons of economy and convenience; this led to more brittle cast iron guns.[8]
Switch to bronze
Meanwhile, the West Point Foundry produced four bronze 6-pounders in 1834, of which three were rejected on sight.[9] In 1835, the US Army Ordnance Board meeting in Watervliet, New York decided to switch to bronze field guns. In July 1836, two established bronze foundries, Cyrus Alger & Company of Boston and N. P. Ames of Cabotville, Massachusetts were hired to manufacture bronze 6-pounder guns. Alger produced 26 and Ames produced 32 bronze Model 1835 6-pounder guns.[8] The Model 1838 bronze 6-pounder was a lighter cannon designed for horse artillery units. Alger delivered 62 and Ames delivered 36 of the Model 1838 gun. Ames also manufactured 27 Model 1840 bronze 6-pounders, which were heavier than the Model 1838.[10]
The Model 1841 bronze 6-pounder cannon proved to be the most successful. The gun was not officially discarded by the US Army until 1868 though none were produced after 1862. Ames manufactured at least 646 Model 1841 guns and Alger produced at least 337. Of the latter group, 10 were so-called Cadet guns which weighed only 570 lb (258.5 kg). There were no recorded losses during proofing, though some of the guns varied as much as 10 lb (4.5 kg) from the official weight.[8] Four of the Cadet guns were produced for the Virginia Military Institute, two for the Arkansas Military Institute, and four for the Georgia Military Institute. [11] The Eagle Foundry of Miles Greenwood of Cincinnati delivered 97 bronze 6-pounders of which 43 were rifled between August 1861 and December 1862. The Western Foundry of William D. Marshall & Company of St. Louis manufactured 33 bronze 6-pounders of which six were rifled between December 1861 and May 1862. Henry N. Hooper & Company of Boston produced eight bronze 6-pounders and Revere Copper Company of Boston delivered two similar guns in February 1862.[12]
| Description | No. Accepted | Base ring diameter | Length w/o knob | Bore length | Bore len. in calibers | Weight of barrel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1835 | 58 | 9.8 in (24.9 cm) | 60 in (152.4 cm) | 57.5 in (146.1 cm) | 15.7 | 743 lb (337.0 kg) |
| Model 1838 | 98 | 9.8 in (24.9 cm) | 53.75 in (136.5 cm) | 51.25 in (130.2 cm) | 14.0 | 690 lb (313.0 kg) |
| Model 1840 | 27 | 10.3 in (26.2 cm) | 53.75 in (136.5 cm) | 51.25 in (130.2 cm) | 14.0 | 812 lb (368.3 kg) |
| Model 1841 | 854+ | 10.3 in (26.2 cm) | 60 in (152.4 cm) | 57.5 in (146.1 cm) | 15.7 | 880 lb (399.2 kg) |
| Cadet guns | 10 | 9.53 in (24.2 cm) | 46 in (116.8 cm) | 43 in (109.2 cm) | 11.7 | 570 lb (258.5 kg) |
Specifications
The Model 1841 bronze 6-pounder gun barrel was 60 in (152.4 cm) from the base ring to the muzzle and weighed 880 lb (399.2 kg). The diameter of the bore (caliber) was 3.67 in (9.32 cm) and the bore length was 57.5 in (146.1 cm). This means the bore was 15.67 calibers long.[14] The cannon fired a 6.1 lb (2.8 kg) round shot that was 3.58 in (9.09 cm) in diameter. At 5° elevation, the gun could hurl the round shot a distance of 1,523 yd (1,392.6 m) with the standard firing charge of 1.25 lb (0.6 kg). The 5.5 lb (2.5 kg) spherical case shot released 37 musket balls when it burst. At 4° elevation, the gun could throw the spherical case round a distance of 1,200 yd (1,097.3 m). The 7 lb (3.2 kg) canister shot contained 48 cast iron balls that were 1.15 in (2.92 cm) in diameter.[15] Canister shot was effective up to a distance of 350 yd (320 m).[16]
A 6-pounder battery typically included four 6-pounder field guns and two M1841 12-pounder howitzers. Altogether, the battery required 14 6-horse teams and seven spare horses.[17] The teams pulled the six artillery pieces and limbers, six caissons, one battery wagon, and one traveling forge. Each caisson weighed 3,800 lb (1,724 kg) and carried two ammunition chests, each with 50 rounds.[18] The carriage for the 6-pounder gun weighed 900 lb (408 kg).[19] A 6-pounder cannon and its limber weighed 3,185 lb (1,445 kg) when fully loaded with one 50-round ammunition chest.[20] The 1850 Ordnance Manual dictated that each ammunition chest hold 35 round shot, five spherical case shot, and 10 canister rounds. The 1862 manual was updated so that each ammunition chest contained 25 round shot, 20 spherical case shot, and five canister rounds.[15] Nine men manned each cannon, the gunner who commanded the gun and eight artillerists who were numbered according to their function.[21]
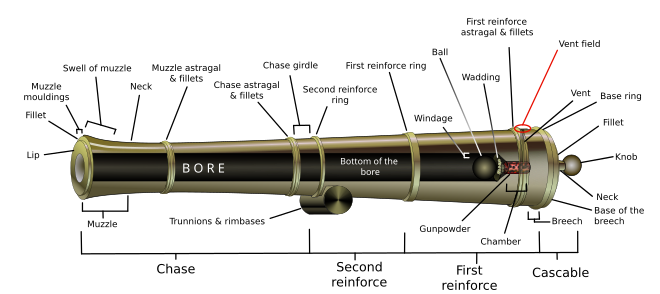
| Description | Dimension |
|---|---|
| Weight of the gun barrel | 880 lb (399.2 kg) |
| Diameter of the bore (caliber) | 3.67 in (9.32 cm) |
| Length of the bore | 57.5 in (146.1 cm) |
| Length of the bore in calibers | 15.7 |
| Length from the rear of the base ring to the face of the muzzle | 60 in (152.4 cm) |
| Length from the rear of the knob to the face of the muzzle | 65.6 in (166.6 cm) |
| Length from the rear of the base ring to the end of the (second) reinforce | 30 in (76.2 cm) |
| Length of the chase from the end of the reinforce to the rear of the astragal | 22 in (55.9 cm) |
| Length from the rear of the astragal to the face of the muzzle | 8 in (20.3 cm) |
| Length from the rear of the base ring to the rear of the trunnions | 23.25 in (59.1 cm) |
| Diameter of the base ring | 10.3 in (26.2 cm) |
| Thickness of metal at the vent | 3.03 in (7.7 cm) |
| Thickness of metal at the end of the (second) reinforce | 2.415 in (6.1 cm) |
| Thickness of metal at the end of the chase (astragal) | 1.415 in (3.6 cm) |
History
Mexican War

The American bronze 6-pounder field guns saw action at the Battle of Palo Alto on 8 May 1846 during the Mexican–American War. General Zachary Taylor led a force numbering 2,228 troops that included two 18-pounder heavy cannons and two 4-gun light batteries under Major Samuel Ringgold and Captain James Duncan. They were opposed by General Mariano Arista with 365 officers, 3,461 rank and file, eight 4-pounder and two 8-pounder cannons. The action became largely an artillery duel where the American guns proved to be superior. American losses were five killed, 43 wounded, and two missing. However, 10 more soon died of their wounds, including Ringgold who was struck in both knees by a 4-pounder round shot. Arista verbally admitted losing 252 killed, but wrote only 102 killed in his official report. The next morning, the Mexican army withdrew to a second position but it was defeated that day at the Battle of Resaca de la Palma.[22]
At Palo Alto, both Ringgold's and Duncan's batteries maneuvered rapidly and inflicted severe casualties in the Mexican ranks. At the start of the action they deployed 100 yd (91 m) in front of the American infantry. Near the end of the action, under the cover of smoke, Duncan's battery unlimbered 300 yd (274 m) from its opponents and caused the Mexican right flank to pull back.[22] Both Ringgold's and Duncan's batteries were armed with bronze 6-pounder field guns. However, archeological evidence indicates that one or more 12-pounder howitzers may have been used also.[23] The Mexicans employed old French Gribeauval system cannons but they were still effective weapons. However, the inferior Mexican gunpowder caused many rounds to fall short. The Mexican artillery drivers were hired civilians, so that their cannons were much less mobile than those of the well-trained American drivers.[24]
Civil War

The M1841 bronze 6-pounder cannon proved to be an excellent weapon during the Mexican–American War.[15] However, American Civil War combat experience soon showed that bronze smoothbore 6-pounder field guns were no longer effective weapons.[25] When George B. McClellan became commander of the Union Army of the Potomac he ordered that all of the old Model 1841 vintage guns be replaced by 12-pounder Napoleons. The older guns were replaced in the eastern armies first and the older model guns persisted in the western armies for a longer period of time.[26] Surviving records show a westward migration of US Army artillery pieces that had become obsolete. The 6-pounders were quickly replaced by 12-pounder Napoleons, 3-inch Ordnance rifles, 10-pounder Parrott rifles, and other field guns. On 30 June 1863, the Department of the Cumberland reported having 24 smoothbore 6-pounders while the Department of the Ohio had only eight.[25] Rifling was added to bronze 6-pounders, but this experiment was not successful because bronze wears more easily than iron. The rifling eroded rapidly, rendering the guns inaccurate. See James rifle.[27]
Variants of the M1841 bronze 6-pounder were also manufactured in the Confederacy though records are sketchy. Because the South lacked the North's industrial capacity, the 6-pounders were employed by Confederate armies for a longer period. Robert E. Lee wanted the old Model 1841 bronze guns to be melted down and recast into 12-pounder Napoleons. Nevertheless, there were still numbers of the old pieces serving with Southern armies as late as the Battle of Chancellorsville.[26] At the Battle of Antietam on 17 September 1862, there were at least 41 6-pounder guns still being employed in Confederate batteries, while the Union Army of the Potomac had no 6-pounders.[28] For example, the 4th Company, Washington Artillery (Eshleman's) was equipped with two 6-pounders and two 12-pounder howitzers.[29]
During the Battle of Pea Ridge on 7–8 March 1862, both armies still employed significant numbers of smoothbore and rifled 6-pounder field guns. In the Union army, three units were armed with four 6-pounder smoothbores and two 12-pounder howitzers: the 2nd Ohio Battery, 1st Iowa Independent Battery Light Artillery, and 3rd Iowa Independent Battery Light Artillery. The 4th Ohio Battery had four rifled 6-pounders and two 12-pounder howitzers. The 1st Independent Battery Indiana Light Artillery had four rifled and two smoothbore 6-pounder field guns. Battery "A", 2nd Illinois Light Artillery Regiment had two rifled and two smoothbore 6-pounder field guns and two 12-pounder howitzers.[30] In the Confederate army, Clark's, Jackson's, and Gorham's Missouri batteries and Hart's Arkansas Battery each had four 6-pounder smoothbores. Mixed batteries with 6-pounder smoothbores included Provence's Arkansas Battery (2), and Wade's (2), Tull's (2), Guibor's (2), and MacDonald's (1) Missouri batteries. Tull's Battery also had two rifled 6-pounder guns. Kneisley's and Kelly's Missouri batteries had an unknown number of 6-pounders.[31] Kneisley's guns were old cast iron pieces.[32]
Civil War artillery
| Description | Caliber | Tube length | Tube weight | Carriage weight | Shot weight | Charge weight | Range 5° elev. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1841 6-pounder cannon | 3.67 in (9.3 cm) | 60 in (152.4 cm) | 884 lb (401 kg) | 900 lb (408 kg) | 6.1 lb (2.8 kg) | 1.25 lb (0.6 kg) | 1,523 yd (1,393 m) |
| M1841 12-pounder cannon | 4.62 in (11.7 cm) | 78 in (198.1 cm) | 1,757 lb (797 kg) | 1,175 lb (533 kg) | 12.3 lb (5.6 kg) | 2.5 lb (1.1 kg) | 1,663 yd (1,521 m) |
| M1841 12-pounder howitzer | 4.62 in (11.7 cm) | 53 in (134.6 cm) | 788 lb (357 kg) | 900 lb (408 kg) | 8.9 lb (4.0 kg) | 1.0 lb (0.5 kg) | 1,072 yd (980 m) |
| M1841 24-pounder howitzer | 5.82 in (14.8 cm) | 65 in (165.1 cm) | 1,318 lb (598 kg) | 1,128 lb (512 kg) | 18.4 lb (8.3 kg) | 2.0 lb (0.9 kg) | 1,322 yd (1,209 m) |
| M1857 12-pounder Napoleon | 4.62 in (11.7 cm) | 66 in (167.6 cm) | 1,227 lb (557 kg) | 1,128 lb (512 kg) | 12.3 lb (5.6 kg) | 2.5 lb (1.1 kg) | 1,619 yd (1,480 m) |
| 12-pounder James rifle | 3.67 in (9.3 cm) | 60 in (152.4 cm) | 875 lb (397 kg) | 900 lb (408 kg)[34] | 12 lb (5.4 kg) | 0.75 lb (0.3 kg) | 1,700 yd (1,554 m) |
| 3-inch Ordnance rifle | 3.0 in (7.6 cm) | 69 in (175.3 cm) | 820 lb (372 kg) | 900 lb (408 kg)[35] | 9.5 lb (4.3 kg) | 1.0 lb (0.5 kg) | 1,830 yd (1,673 m) |
| 10-pounder Parrott rifle | 3.0 in (7.6 cm) | 74 in (188.0 cm) | 899 lb (408 kg) | 900 lb (408 kg)[35] | 9.5 lb (4.3 kg) | 1.0 lb (0.5 kg) | 1,900 yd (1,737 m) |
| 20-pounder Parrott rifle | 3.67 in (9.3 cm) | 84 in (213.4 cm) | 1,750 lb (794 kg) | 1,175 lb (533 kg)[34] | 20 lb (9.1 kg) | 2.0 lb (0.9 kg) | 1,900 yd (1,737 m) |
Notes
- ^ McConnell 1988, pp. 15–16.
- ^ a b McConnell 1988, p. 392.
- ^ McConnell 1988, pp. 25–27.
- ^ Hazlett, Olmstead & Parks 1983, p. 42.
- ^ Hazlett, Olmstead & Parks 1983, p. 32.
- ^ Hazlett, Olmstead & Parks 1983, pp. 33–36.
- ^ Hazlett, Olmstead & Parks 1983, p. 39.
- ^ a b c Hazlett, Olmstead & Parks 1983, p. 36.
- ^ Hazlett, Olmstead & Parks 1983, p. 35.
- ^ Hazlett, Olmstead & Parks 1983, pp. 38–39.
- ^ Hazlett, Olmstead & Parks 1983, p. 45.
- ^ Hazlett, Olmstead & Parks 1983, pp. 46–47.
- ^ Hazlett, Olmstead & Parks 1983, p. 33.
- ^ a b Hazlett, Olmstead & Parks 1983, p. 41.
- ^ a b c Swain 2011.
- ^ Coggins 1983, p. 67.
- ^ Coggins 1983, p. 73.
- ^ Coggins 1983, p. 68.
- ^ a b Coggins 1983, p. 66.
- ^ Coggins 1983, p. 69.
- ^ Johnson & Anderson 1995, p. 29.
- ^ a b Haecker 1994, pp. Chap.3.
- ^ Haecker 1994, pp. Chap.7.
- ^ Haecker 1994, pp. Chap.4.
- ^ a b Hazlett, Olmstead & Parks 1983, p. 51.
- ^ a b Morgan 2002.
- ^ Hazlett, Olmstead & Parks 1983, p. 52.
- ^ Johnson & Anderson 1995, p. 129.
- ^ Johnson & Anderson 1995, p. 90.
- ^ Shea & Hess 1992, pp. 331–334.
- ^ Shea & Hess 1992, pp. 334–339.
- ^ Shea & Hess 1992, p. 148.
- ^ Coggins 1983, p. 77.
- ^ a b Johnson & Anderson 1995, p. 25.
- ^ a b Hazlett, Olmstead & Parks, p. 217.
References
- Coggins, Jack (1983). Arms and Equipment of the Civil War. New York, N.Y.: Fairfax Press. ISBN 0-517-402351.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Haecker, Charles M. (1994). "A Thunder of Cannon: Archaeology of the Mexican-American War Battlefield of Palo Alto". Santa Fe, N.M.: National Park Service.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Hazlett, James C.; Olmstead, Edwin; Parks, M. Hume (1983). Field Artillery Weapons of the American Civil War. Urbana, Ill.: University of Illinois Press. ISBN 0-252-07210-3.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Johnson, Curt; Anderson, Richard C. Jr. (1995). Artillery Hell: The Employment of Artillery at Antietam. College Station, Tex.: Texas A&M University Press. ISBN 0-89096-623-0.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - McConnell, David (1988). "British Smooth-bore Artillery: A Technological Study to Support Identification, Acquisition, Restoration, Reproduction, and Interpretation of Artillery at National Historic Parks in Canada" (PDF). Ottawa: Minister of Supply and Services Canada.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Morgan, James (2002). "Green Ones and Black Ones: The Most Common Field Pieces of the Civil War". civilwarhome.com.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Swain, Craig (2011). "Mexican War to Civil War - The Model 1841 6-pdr Field Gun".
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Shea, William L.; Hess, Earl J. (1992). Pea Ridge: Civil War Campaign in the West. Chapel Hill, N.C.: The University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 0-8078-4669-4.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
Further reading
- Downey, Brian (2019). "The Weapons of Antietam". Antietam on the Web.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Cole, Philip M. (2002). Civil War Artillery at Gettysburg. New York, N.Y.: Da Capo Press. ISBN 0-306-81145-6.
- Ripley, Warren (1984). Artillery and Ammunition of the Civil War. Charleston, S.C.: The Battery Press. OCLC 12668104.
External links
- "Model 1841 6-Pounder Towed Field Gun". Military Factory. 2019.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
