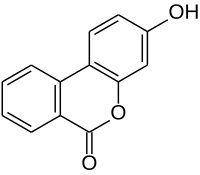
Urolithin B
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-Hydroxybenzo[c]chromen-6-one
| |
| Other names
Uro-B
3-Hydroxyurolithin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.236.446 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 212.204 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Urolithin B is an urolithin, a type of phenolic compounds produced in the human gut after absorption of ellagitannins-containing food such as pomegranate,[1] strawberries, red raspberries, walnuts or oak-aged red wine.[2] Urolithin B is found in the urine in the form of urolithin B glucuronide.
See also
References
- ^ Bialonska D, Kasimsetty SG, Khan SI, Ferreira D (11 November 2009). "Urolithins, intestinal microbial metabolites of Pomegranate ellagitannins, exhibit potent antioxidant activity in a cell-based assay". J Agric Food Chem. 57 (21): 10181–6. doi:10.1021/jf9025794. PMID 19824638.
- ^ Cerdá, Begoña; Tomás-Barberán, Francisco A.; Espín, Juan Carlos (2005). "Metabolism of Antioxidant and Chemopreventive Ellagitannins from Strawberries, Raspberries, Walnuts, and Oak-Aged Wine in Humans: Identification of Biomarkers and Individual Variability". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 53 (2): 227–235. doi:10.1021/jf049144d. PMID 15656654.
External links
