Angeli's salt
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| N2Na2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 121.991 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
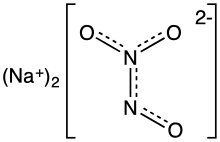
Angeli's salt, sodium trioxodinitrate, is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2[N2O3]. It contains nitrogen in an unusual reduced state. It is a colorless, water-soluble solid, a salt. In research, this salt is used as a source of the metastable nitroxyl (HNO), which is a signalling molecule in nature.[1] It is also known by the name sodium trioxodinitrate(II) monohydrate.
As first reported by Angelo Angeli in 1896, the salt is prepared by combining hydroxylamine and an organic nitrate, as a source of NO2+:[2][3]
- NH2OH + RONO2 + 2 NaOR' → ROH + 2 R'OH + Na2N2O3
The structure of the hydrate has been confirmed by X-ray crystallography. The anion is planar. Starting from the ONN end, the bond distances are 1.35 (N-O), 1.26 (N-N), 1.31 (N-O), 1.32 Å (N-O). Negative charge is on the oxygen atoms at opposite ends of the molecule. The angles are single oxygen to nitrogen-nitrogen bond 112.9°, nitrogen-nitrogen bond to trans oxygen 118.4°, nitrogen-nitrogen bond to cis oxygen 122.5°. This means that the nitrogen-nitrogen bond is a double bond, and that the cis oxygen is slightly repelled by the single oxygen.[4]
Reaction of Angeli's salt with secondary amines in the presence of a proton source results in extrusion of N2 via isodiazenes as proposed intermediates.[5]
References
- ^ Nakagawa, H. (2013). "Controlled release of HNO from chemical donors for biological applications". J. Inorg. Biochem. 118: 187–190. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2012.10.004. PMID 23140899.
- ^ A. Angeli (1896). "Sopra la nitroidrossilammina". Gazz. Chim. Ital. 26: 17–28.
- ^ Hughes, Martin N.; Cammack, Richard (1999). "Synthesis, chemistry, and Applications of Nitroxyl Ion Releasers Sodium Trioxodinitrate or Angeli's Salt and Piloty's Acid". Methods in Enzymology (Nitric Oxide, Part C: Biological and Antioxidant Activities). 301: 279–287. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(99)01092-7. PMID 9919577.
- ^ Hope, Hakon; Sequeira, Michael R. (February 1973). "Angeli's salt. Crystal structure of sodium trioxodinitrate(II) monohydrate, Na2N2O3.H2O". Inorganic Chemistry. 12 (2): 286–288. doi:10.1021/ic50120a008.
- ^ 1937-, Carey, Francis A. (2007). Advanced organic chemistry. Part B, Reactions and synthesis. Sundberg, Richard J., 1938- (5th ed.). New York, NY: Springer. ISBN 9781601195494. OCLC 223941000.
{{cite book}}:|last=has numeric name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
