Isosakuranetin
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
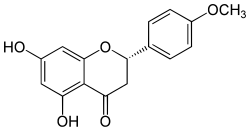
| IUPAC name
(2S)-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydrochromen-4-one
| |
| Other names
4'-Methylnaringenin
4'-Methoxy-5,7-dihydroxyflavonone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.866 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H14O5 | |
| Molar mass | 286.27 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Isosakuranetin, an O-methylated flavonoid, is the 4'-methoxy derivative of naringenin, a flavanone. Didymin, a disaccharide of isosakuranetin, occur e.g. in sweet orange, blood orange and mandarin.[1]
Glycosides
- Poncirin is the 7-O-neohesperidoside of isosakuranetin.
- Didymin is the 7-O-rutinoside of isosakuranetin
References
- ^ "Polyphenols in Human Health and Disease" ISBN 9780123984562
