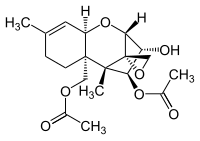
Diacetoxyscirpenol
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
anguidine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.159 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H26O7 | |
| Molar mass | 366.410 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Diacetoxyscirpenol (DAS), also called anguidine, is a mycotoxin from the group of type A trichothecenes. It is a secondary metabolite product of fungi of the genus Fusarium and may cause toxicosis in farm animals.[1]
References
