Aranyos Seat
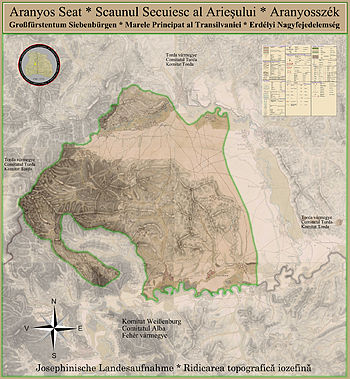
Aranyos seat (Hungarian: Aranyosszék; Latin: Sedes Aurata; Romanian: Scaunul Arieşului)[1] was the seat (territorial administrative unit) of the Transylvanian Székelys living in the Valley of the Arieş River (Hungarian: Aranyos).
The free Székely Guards were granted a part of the lands belonging to the king around the old Turda Castle (in ruins, today in the Moldovenești area), as a reward for the courage they showed in battles against Tatars. Here they settled in 21 villages, in around 1270. This was the newest Székely Seat, because the other Székely territories (today: Székely Land) were populated earlier.
The centre of the seat was a small market town (oppidum), Felvinc, now Unirea village.
In the late 19th century, when the administrative system of the Kingdom of Hungary was reorganised, the Seat was united with Torda County and Torda-Aranyos County was created.
The region is today part of the Alba and Cluj Counties in Romania. The settlements, current or former, are now in the following localities: Lunca Mureșului, Ocna Mureș, Mirăslău, Rimetea and Unirea in Alba County; and Călărași, Mihai Viteazu, Moldovenești and Turda in Cluj County.
See also
References
- ^ Attila M. Szabó: Historical and Administrative Toponymy of Transylvania, the Banat and Partium. Miercurea-Ciuc, 2003, pp. II/1079-80.
