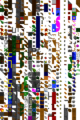Texture atlas
In computer graphics, a texture atlas (also called a sprite sheet or an image sprite) is an image containing multiple smaller images, usually packed together to reduce overall dimensions.[1] An atlas can consist of uniformly-sized images or images of varying dimensions.[1] A sub-image is drawn using custom texture coordinates to pick it out of the atlas.
Benefits
In an application where many small textures are used frequently, it is often more efficient to store the textures in a texture atlas which is treated as a single unit by the graphics hardware. This reduces the overhead of a context switch by increasing memory locality. Careful alignment may be needed to avoid bleeding between sub textures when used with mipmapping and texture compression.
In web development, images are packed into a sprite sheet to reduce the number of image resources that need to be fetched in order to display a page.[2]
Gallery
-
A texture atlas for a video game
-
A texture atlas of glyphs
-
Sprite sheet for the video game Blades of Exile
References
- ^ a b "SDK White Paper Improve Batching Using Texture Atlases" (PDF). Nvidia. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
- ^ "Implementing image sprites in CSS". Mozilla Development Network.
External links
Explanations and algorithms
- Texture Atlas Whitepaper - A whitepaper by NVIDIA which explains the technique.
- Practical Texture Atlases - A guide on using a texture atlas (and the pros and cons).
- A thousand ways to pack the bin - Review and benchmark of the different packing algorithms
- Sprite Sheets - Essential Facts Every Game Developer Should Know - Funny video explaining the benefits of using sprite sheets
Tools
- TexturePacker - sprite sheet packer with graphical user interface and tons of options. Works with almost all game engines.
- LibGDX texture packer - Open source texture packer utility from libGDX
- Texture Atlas Maker - Open source texture atlas utility for 2D OpenGL games.
- SpriteMapper - Open source texture atlas (sprite map) utility including an Apache Ant task.