Thioproscaline
Appearance
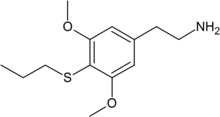
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-[3,5-dimethoxy-4-(propylsulfanyl)phenyl]ethanamine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H21NO2S | |
| Molar mass | 255.376 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Thioproscaline, or 3,5-dimethoxy-4-propylthiophenethylamine, is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is the 4-propylthio analog of mescaline. Thioproscaline was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines i Have Known And Loved), the dosage range is listed as 20–25 mg, and the duration listed as 10–15 hours. Thioproscaline causes closed-eye visuals, slight open-eye visuals, and a body load. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of thioproscaline.
See also
External links
