Wieacker syndrome
Appearance
| Wieacker syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Intellectual disability-developmental delay-contractures syndrome |
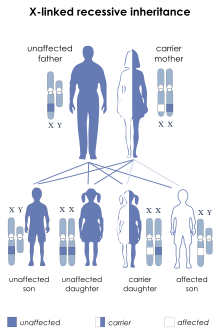 | |
| This condition is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner. | |
Wieacker Syndrome or Wieacker-Wolff syndrome is a rare, severely disabling, genetic disorder. It is an X-linked recessive disorder and thus affects mostly males.
Presentation
The condition is characterized by contracture of the lower joints, muscle atrophy, impaired facial muscles, mental retardation, and syndromic facies.[1][2] Heterozygous females may show mild signs of the disease.
Genetics
Wieacker syndrome is caused by a mutation in ZC4H2 on the X chromosome (Xq13-q21).[2]
Diagnosis
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (December 2017) |
Treatment
Treatment is supportive in nature. There are no effective disease-modifying therapies.[2]
Epidemiology
Fewer than 30 cases have been identified.[3]
References
- ^ "OMIM Entry # 314580 - WIEACKER-WOLFF SYNDROME; WRWF". www.omim.org.
- ^ a b c "Wieacker Syndrome - NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders)".
- ^ RESERVED, INSERM US14 -- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Intellectual disability developmental delay contractures syndrome". www.orpha.net.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
