Bit Agusi
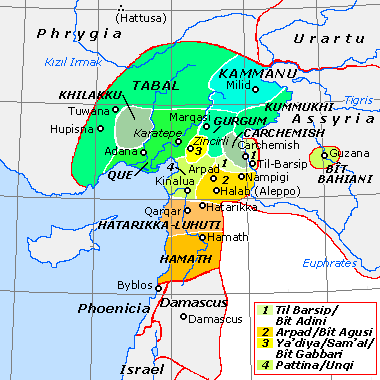
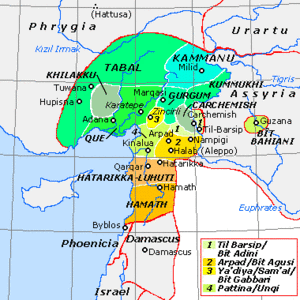
Bit Agusi or Bit Agushi (also written Bet Agus) was an ancient Aramaean Syro-Hittite state, established by Gusi of Yakhan at the beginning of the 9th century BC. It had included the cities of Arpad, Nampigi (Nampigu) and later on Aleppo.[1] Arpad was the capital of the state-kingdom.[2] Bit Agusi stretched from the A'zaz area in the north to Hamath in the south.[3]
Decline and fall
Arpad later became a major vassal city of the Kingdom of Urartu. In 743 BC, during the Urartu-Assyria War, the Neo-Assyrian king Tiglath-Pileser III laid siege to Arpad following the defeat of the Urartian army of Sarduri II at Samsat. But the city of Arpad did not surrender easily. It took Tiglath-Pileser three years of siege to conquer Arpad, whereupon he massacred its inhabitants and destroyed the city.[4] Afterward Arpad served a provincial capital.[5] The remains of Arpad's walls are still preserved in Tell Rifaat to the height of 8 meters.[6] A coalition of princes which had been allied to the city was also defeated, including the kings of Kummuh, Quwê, Carchemish and Gurgum. Bit Agusi was never repopulated.
See also
References
- ^ Agusi Arpad, Syria
- ^ Lipinsky, Edward (2000). The Aramaeans: Their Ancient History, Culture, Religion (Peeters) p. 195.
- ^ Lipinsky, 2000, p. 99.
- ^ Healy, Mark (1992). The Ancient Assyrians (Osprey) p. 25.
- ^ Kipfer, Barbara Ann (2000). Encyclopedic Dictionary of Archaeology. p. 626.
- ^ Lipinsky, 2000, p. 529.