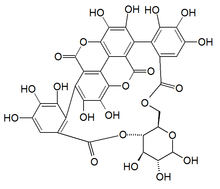
Punicalin
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
4,6-(S,S)-Gallagyl-D-glucose
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C34H22O22 | |
| Molar mass | 782.52 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Punicalin is an ellagitannin. It can be found in Punica granatum (pomegranate)[1] or in the leaves of Terminalia catappa, a plant used to treat dermatitis and hepatitis.[2][3] It is also reported in Combretum glutinosum, all three species being Myrtales, the two last being Combretaceae.
It is a highly active carbonic anhydrase inhibitor.[4]
Chemistry
The molecule contains a gallagic acid component linked to a glucose.
References
- ^ Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Lee, R. P.; Henning, S. M.; Heber, D. (2009). "Absence of Pomegranate Ellagitannins in the Majority of Commercial Pomegranate Extracts: Implications for Standardization and Quality Control". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 57 (16): 7395–7400. doi:10.1021/jf9010017. PMID 20349921.
- ^ Lin, C. C.; Hsu, Y. F.; Lin, T. C.; Hsu, F. L.; Hsu, H. Y. (1998). "Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity of punicalagin and punicalin on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage in rats". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 50 (7): 789–794. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1998.tb07141.x. PMID 9720629. S2CID 8639399.
- ^ Lin, Chun-Ching; Hsu, YF; Lin, TC (1999). "Effects of punicalagin and punicalin on carrageenan-induced inflammation in rats". The American Journal of Chinese Medicine. 27 (3 & 4): 371–376. doi:10.1142/S0192415X99000422. PMID 10592846.
- ^ Satomi, H.; Umemura, K.; Ueno, A.; Hatano, T.; Okuda, T.; Noro, T. (1993). "Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors from the pericarps of Punica granatum L". Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 16 (8): 787–790. doi:10.1248/bpb.16.787. PMID 8220326.
