749 Malzovia
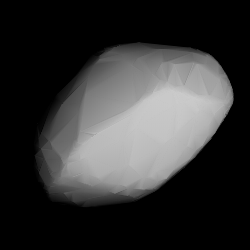 Modelled shape of Malzovia from its lightcurve | |
| Discovery [1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | S. Belyavskyj |
| Discovery site | Simeiz Obs. |
| Discovery date | 5 April 1913 |
| Designations | |
| (749) Malzovia | |
Named after | Nikolai Maltsov [2] (Russian amateur astronomer) |
| A913 GD · 1950 JO 1968 XA · 1913 RF | |
| Orbital characteristics [3] | |
| Epoch 31 May 2020 (JD 2459000.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 107.00 yr (39,080 d) |
| Aphelion | 2.6316 AU |
| Perihelion | 1.8558 AU |
| 2.2437 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.1729 |
| 3.36 yr (1,228 d) | |
| 289.14° | |
| 0° 17m 35.88s / day | |
| Inclination | 5.3946° |
| 109.76° | |
| 128.97° | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| 5.9274±0.0002 h[10][a] | |
Pole ecliptic latitude | |
749 Malzovia (prov. designation: A913 GD or 1913 RF) is a stony background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 11 kilometers (6.8 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 5 April 1913, by Russian astronomer Sergey Belyavsky at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula.[1] The elongated S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 5.9 hours. It was named after Russian amateur astronomer Nikolai Maltsov (S. I. Maltsov) who founded the discovering Simeïs Observatory in 1900.[2]
Orbit and classification
Located in the region of the Flora family (402),[12] a giant asteroid family and the largest family of stony asteroids, Malzovia is a non-family asteroid of the main belt's background population when applying the hierarchical clustering method to its proper orbital elements.[4][5][6] It orbits the Sun in the inner main-belt at a distance of 1.9–2.6 AU once every 3 years and 4 months (1,228 days; semi-major axis of 2.24 AU). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.17 and an inclination of 5° with respect to the ecliptic.[3] The body's observation arc begins at the German Heidelberg Observatory on 30 April 1913, or 25 days after its official discovery observation at Simeiz Observatory.[1]
Naming
This minor planet was named after Russian amateur astronomer Nikolai Sergeevich Maltsov (S. I. Malzov) who founded the discovering Simeiz Observatory, which he later donated to the Pulkovo Observatory in 1911. Malzov was a close friend of Sergey Belyavsky and of Oskar Backlund, after whom asteroid 856 Backlunda was named. After World War I, Malzov lived at Menton, on the French Riviera near Italy. The naming citation was mentioned in The Names of the Minor Planets by Paul Herget in 1955 (H 75).[2]
Physical characteristics
In the Tholen and Bus–Binzel SMASS classification, Malzovia is a common, stony S-type asteroid.[3]
Rotation period
In February 2020, a rotational lightcurve of Malzovia was obtained from photometric observations by French amateur astronomer René Roy. Lightcurve analysis gave a well-defined rotation period of (5.9274±0.0002) hours with a high brightness variation of 0.50±0.02 magnitude, indicative of its elongated shape (U=3).[10] Alternative period determinations by Julian Oey and Frederick Pilcher in May 2014 gave very similar results of (5.9275±0.0002) and (5.9279±0.0001) hours, respectively, both with an amplitude of 0.30 magnitude (U=3−/3−).[13][14][a]
Poles
Published in 2018, thermophysical modeling of Malzovia from thermal data obtained from the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) gave a sidereal period of (5.92748±0.00002 h) and two spin axes at (53.0°, 37.0°) and (242.0°, 46.0°) in ecliptic coordinates (λ, β).[11] Previously, two lightcurves published in 2016, using modeled photometric data from the Lowell Photometric Database (LPD) and other sources, gave a period of (5.92749±0.00001) and 5.92748±0.00005 hours, respectively. Each modeled lightcurve also determined two poles at (53.0°, 37.0°) and (242.0°, 46.0°), as well as (55.0°, 46.0°) and (246.0°, 55.0°), respectively.[15][16]
Diameter and albedo
According to the surveys carried out by the Japanese Akari satellite and the NEOWISE mission of NASA's WISE telescope, Malzovia measures (11.065±0.071) and (12.13±0.26 km) kilometers in diameter and its surface has a low albedo of (0.270±0.029) and (0.239±0.011), respectively.[7][8][9]
The Collaborative Asteroid Lightcurve Link assumes an albedo of 0.24 and calculates a diameter of 12.98 kilometers based on an absolute magnitude of 11.6.[12] The WISE team also published several alternative mean-diameters of (11.11±2.12 km), (11.658±2.526 km) and (11.724±0.056 km), with a corresponding albedo of (0.41±0.12), (0.351±0.144) and (0.2444±0.0464).[5][12]
Notes
- ^ a b Lightcurve plot of (749) Malzovia, by Frederick Pilcher (2014) at the Organ Mesa Observatory (G50) in Arizona. Rotation period 5.9279±0.0001 hours with a brightness amplitude of 0.30±0.03 mag. Quality code is 3–. Summary figures at the LCDB and ASLC website.
References
- ^ a b c d e "749 Malzovia (A913 GD)". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- ^ a b c Schmadel, Lutz D. (2007). "(749) Malzovia". Dictionary of Minor Planet Names. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. p. 71. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-29925-7_750. ISBN 978-3-540-00238-3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 749 Malzovia (A913 GD)" (2020-04-28 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- ^ a b "Asteroid 749 Malzovia – Proper Elements". AstDyS-2, Asteroids – Dynamic Site. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- ^ a b c "Asteroid 749 Malzovia". Small Bodies Data Ferret. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- ^ a b Zappalà, V.; Bendjoya, Ph.; Cellino, A.; Farinella, P.; Froeschle, C. (1997). "Asteroid Dynamical Families". NASA Planetary Data System: EAR-A-5-DDR-FAMILY-V4.1. Retrieved 5 June 2020.} (PDS main page)
- ^ a b c d Mainzer, A. K.; Bauer, J. M.; Cutri, R. M.; Grav, T.; Kramer, E. A.; Masiero, J. R.; et al. (June 2016). "NEOWISE Diameters and Albedos V1.0". NASA Planetary Data System. Bibcode:2016PDSS..247.....M. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- ^ a b c Masiero, Joseph R.; Grav, T.; Mainzer, A. K.; Nugent, C. R.; Bauer, J. M.; Stevenson, R.; et al. (August 2014). "Main-belt Asteroids with WISE/NEOWISE: Near-infrared Albedos". The Astrophysical Journal. 791 (2): 11. arXiv:1406.6645. Bibcode:2014ApJ...791..121M. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/791/2/121.
- ^ a b c d Usui, Fumihiko; Kuroda, Daisuke; Müller, Thomas G.; Hasegawa, Sunao; Ishiguro, Masateru; Ootsubo, Takafumi; et al. (October 2011). "Asteroid Catalog Using Akari: AKARI/IRC Mid-Infrared Asteroid Survey". Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan. 63 (5): 1117–1138. Bibcode:2011PASJ...63.1117U. doi:10.1093/pasj/63.5.1117. Retrieved 5 June 2020. (online, AcuA catalog p. 153)
- ^ a b Behrend, Raoul. "Asteroids and comets rotation curves – (749) Malzovia". Geneva Observatory. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- ^ a b c Hanuš, J.; Delbo', M.; Ďurech, J.; Alí-Lagoa, V. (July 2018). "Thermophysical modeling of main-belt asteroids from WISE thermal data". Icarus. 309: 297–337. arXiv:1803.06116. Bibcode:2018Icar..309..297H. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2018.03.016. ISSN 0019-1035.
- ^ a b c "LCDB Data for (749) Malzovia". Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB). Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- ^ Oey, Julian (January 2016). "Lightcurve Analysis of Asteroids from Blue Mountains Observatory in 2014" (PDF). Minor Planet Bulletin. 43 (1): 45–51. Bibcode:2016MPBu...43...45O. ISSN 1052-8091.
- ^ Pilcher, F. (October 2014). "Rotation Period Determinations for 24 Themis, 65 Cybele, 108 Hecuba, 530 Turandot, and 749 Malzovia" (PDF). Minor Planet Bulletin. 41 (4): 250–252.
- ^ Ďurech, J.; Hanuš, J.; Oszkiewicz, D.; Vančo, R. (March 2016). "Asteroid models from the Lowell photometric database". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 587: A48. arXiv:1601.02909. Bibcode:2016A&A...587A..48D. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201527573. ISSN 0004-6361.
- ^ Hanus, J.; Durech, J.; Oszkiewicz, D. A.; Behrend, R.; Carry, B.; Delbo, M.; et al. (February 2016). "New and updated convex shape models of asteroids based on optical data from a large collaboration network" (PDF). Astronomy and Astrophysics. 586: 24. arXiv:1510.07422. Bibcode:2016A&A...586A.108H. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201527441. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
External links
- Lightcurve Database Query (LCDB), at www.minorplanet.info
- Dictionary of Minor Planet Names, Google books
- Asteroids and comets rotation curves, CdR – Geneva Observatory, Raoul Behrend
- Discovery Circumstances: Numbered Minor Planets (1)-(5000) – Minor Planet Center
- 749 Malzovia at AstDyS-2, Asteroids—Dynamic Site
- 749 Malzovia at the JPL Small-Body Database
