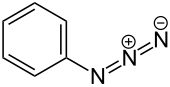
Phenyl azide
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Azidobenzene[1] | |||
| Other names
Phenyl azide[1]
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.756 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| MeSH | C014747 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H5N3 | |||
| Molar mass | 119.127 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Pale yellow, oily liquid | ||
| Boiling point | 49 to 50 °C (120 to 122 °F; 322 to 323 K) at 5 mmHg | ||
| not appreciable | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
explosive | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
Aniline Nitrobenzene Nitrosobenzene Phenylhydrazine Phenylhydroxylamine Diazonium cation | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Phenyl azide is an organic compound with the formula C6H5N3. It is one of the prototypical organic azides. It is a pale yellow oily liquid with a pungent odor. The structure consists of a linear azide substituent bound to a phenyl group. The C−N=N angle is approximately 120°.
Preparation
Phenyl azide is prepared by the diazotization of phenylhydrazine with nitrous acid:[2]
- C6H5NHNH2 + HNO2 → C6H5N3 + 2 H2O
Aryl iodides bearing electron-withdrawing substituents undergo metathesis with sodium azide in the presence of Cu(I), sodium ascorbate, and N,N'-dimethylethane-1,2-diamine (DMEDA):[3]
- RC6H4I + NaN3 → RC6H4N3 + NaI
Chemical reactions
C6H5N3 is used to make heterocycles via cycloaddition to alkenes and especially alkynes, particularly those bearing electronegative substituents. It reacts with triphenylphosphine to give the Staudinger reagent triphenylphosphine phenylimide (C6H5NP(C6H5)3). Thermolysis induces loss of N2 to give the highly reactive phenylnitrene C6H5N.[4]
Phenyl azide and its analogues undergo the azide alkyne Huisgen cycloaddition, a classic example of click chemistry. For example, phenyl azide and phenylacetylene give diphenyl triazole.
Safety
As with many other azides, phenyl azide poses a risk of explosion,[2] so a protective blast shield is recommended during purification and handling. Distillation temperatures should be as low a possible. Organic Syntheses recommends a vacuum of 5mm Hg to give a boiling point of "66–68 °C/21 mm. with a bath temperature of 70–75 °C."[2] The pure substance may be stored in the dark, cold, and even then the shelf-life is only weeks.
References
- ^ a b Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. pp. 66, 1119. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b c R. O. Lindsay and C. F. H. Allen (1955). "Phenyl azide". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 3, p. 710.
- ^ Andersen, Jacob; Madsen, Ulf; Björkling, Fredrik; Liang, Xifu (2005). "Rapid Synthesis of Aryl Azides from Aryl Halides under Mild Conditions". Synlett. 2005 (14): 2209–2213. doi:10.1055/s-2005-872248. ISSN 0936-5214.
- ^ W. H. Pearson, P. S. Ramamoorthyin "Phenyl Azide" Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis (Ed: L. Paquette) 2004, J. Wiley & Sons, New York. doi:10.1002/047084289X.