Search results
Appearance
Did you mean: radiative emission
The page "Radioactive emission" does not exist. You can create a draft and submit it for review or request that a redirect be created, but consider checking the search results below to see whether the topic is already covered.
- Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable...95 KB (9,766 words) - 03:59, 21 August 2024
- A radioactive tracer, radiotracer, or radioactive label is a synthetic derivative of a natural compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced...19 KB (2,378 words) - 14:21, 5 June 2024
- Proton emission (also known as proton radioactivity) is a rare type of radioactive decay in which a proton is ejected from a nucleus. Proton emission can...5 KB (478 words) - 23:39, 11 August 2024
- Radionuclide (redirect from Radioactive isotopes)During those processes, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. These emissions are considered ionizing radiation because they are energetic...31 KB (2,660 words) - 14:00, 10 June 2024
- Neutron emission is a mode of radioactive decay in which one or more neutrons are ejected from a nucleus. It occurs in the most neutron-rich/proton-deficient...7 KB (871 words) - 22:07, 1 December 2023
- Positron emission, beta plus decay, or β+ decay is a subtype of radioactive decay called beta decay, in which a proton inside a radionuclide nucleus is...9 KB (1,138 words) - 15:26, 15 August 2024
- Nuclear fission product (redirect from Radioactive product)the 90Sr atoms have decayed, emitting only 0.4% of the betas. The radioactive emission rate is highest for the shortest lived radionuclides, although they...42 KB (5,142 words) - 10:07, 17 March 2024
- Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes...73 KB (8,763 words) - 14:26, 28 August 2024
- early 1960s, there was greater sensitivity about the dangers of radioactive emissions in the atmosphere, and devising an appropriate test plan for the...40 KB (5,588 words) - 02:39, 3 April 2024
- Nuclear medicine (redirect from Radioactive imaging)or nucleology, is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging...39 KB (4,408 words) - 06:50, 28 May 2024
- of TNT equivalent is defined as 4.184 gigajoules (1 gigacalorie). Radioactive emission to the atmosphere aside from prompt neutrons, where known. The measured...38 KB (1,916 words) - 19:57, 30 August 2024
- Beta decay (redirect from Beta emission)elements polonium and radium. In 1899, Ernest Rutherford separated radioactive emissions into two types: alpha and beta (now beta minus), based on penetration...58 KB (6,985 words) - 03:44, 27 August 2024
- of TNT equivalent is defined as 4.184 gigajoules (1 gigacalorie). Radioactive emission to the atmosphere aside from prompt neutrons, where known. The measured...19 KB (1,354 words) - 07:30, 4 September 2024
- Potassium-40 undergoes three types of radioactive decay. In about 89.28% of events, it decays to calcium-40 (40Ca) with emission of a beta particle (β−, an electron)...8 KB (866 words) - 01:37, 24 August 2024
- Nuclear fallout (redirect from Radioactive Fallout)Nuclear fallout is residual radioactive material propelled into the upper atmosphere following a nuclear blast, so called because it "falls out" of the...83 KB (9,837 words) - 12:39, 11 September 2024
- percentage (about 1%) escapes containment and is considered a routine radioactive emission (also higher than from an LWR of comparable size). Responsible operation...76 KB (9,587 words) - 03:19, 3 September 2024
- Gamma ray (redirect from Gamma emission)forms of decay occur, such as alpha or beta decay. A radioactive nucleus can decay by the emission of an α or β particle. The daughter nucleus that results...60 KB (7,399 words) - 18:10, 9 September 2024
- Radiation (redirect from Radioactive radiation)In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes: electromagnetic...47 KB (6,147 words) - 19:47, 14 August 2024
- Alpha decay (redirect from Alpha emission)Alpha decay or α-decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus) and thereby transforms or "decays"...19 KB (2,542 words) - 00:16, 9 September 2024
- of TNT equivalent is defined as 4.184 gigajoules (1 gigacalorie). Radioactive emission to the atmosphere aside from prompt neutrons, where known. The measured...19 KB (1,592 words) - 20:21, 6 June 2024
- (Suppression of Misuse of Radioactive Material) Act 2017 (2017) Parliament of Singapore 3247927Terrorism (Suppression of Misuse of Radioactive Material) Act 20172017Parliament
- energy concerns, that radioactive substances causing the energy to be produced from the environment, outside of the radioactive material. Marie Curie
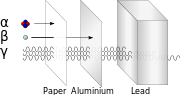
- 'Radioactivity' is a catch-all term for several different emissions from the nuclei of 'radioactive' atoms. There are three main types of radiation: alpha