Osteoma
| Osteoma | |
|---|---|
 | |
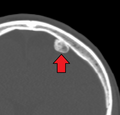
| Osteoma of external auditory meatus | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
An osteoma (plural: "osteomata") is a new piece of bone usually growing on another piece of bone, typically the skull. It is a benign tumor.
When the bone tumor grows on other bone it is known as "homoplastic osteoma"; when it grows on other tissue it is called "heteroplastic osteoma".
Osteoma represents the most common benign neoplasm of the nose and paranasal sinuses. The cause of osteomata is uncertain, but commonly accepted theories propose embryologic, traumatic, or infectious causes. Osteomata are also found in Gardner's syndrome. Larger craniofacial osteomata may cause facial pain, headache, and infection due to obstructed nasofrontal ducts. Often, craniofacial osteoma presents itself through ocular signs and symptoms (such as proptosis).[1]
Variants
- "Osteoma cutis, but there is currently no way of detecting if and when this is likely to occur.
- "Fibro-osteoma"
- "Chondro-osteoma"
-
Osteoma of the frontal sinus seen on x-ray
-
Osteoma of the frontal sinus on CT
-
Osteoma
See also
References
- ^ Michael S. Schwartz, MD; Dennis M. Crockett, MD. "Management of a Large Frontoethmoid Osteoma with Sinus Cranialization and Cranial Bone Graft Reconstruction". International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology.