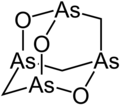
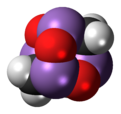
Arsenicin A
Appearance
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,4,6-Trioxa-1,3,5,7-tetraarsatricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decane
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H6As4O3 | |||
| Molar mass | 389.764 g·mol−1 | ||
| Melting point | 182 to 184 °C (360 to 363 °F; 455 to 457 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Arsenicin A is a naturally occurring organoarsenic compound with molecular formula C3H6As4O3. It was first isolated from the New Caledonian marine sponge Echinochalina bargibanti.[1] The compound was characterized by computational and spectroscopic[2][3] techniques and found to possess a cage-like structure similar to adamantane in which the four methanetriyl carbon bridgeheads are replaced by arsenic atoms and three of the six methylene bridges are replaced by oxygen atoms. It is the first polyarsenic compound ever found in nature.[1] Subsequently, the proposed structure was prepared in large quantities via total synthesis and the structure was confirmed by x-ray crystallography.[4]
References
- ^ a b Mancini, Ines; Guella, Graziano; Frostin, Maryvonne; Hnawia, Edouard; Laurent, Dominique; Debitus, Cecile; Pietra, Francesco (2006). "On the First Polyarsenic Organic Compound from Nature: Arsenicin a from the New Caledonian Marine Sponge Echinochalina bargibanti". Chemistry - A European Journal. 12 (35): 8989–94. doi:10.1002/chem.200600783. PMID 17039560.
- ^ Tähtinen, Petri; Saielli, Giacomo; Guella, Graziano; Mancini, Ines; Bagno, Alessandro (2008). "Computational NMR Spectroscopy of Organoarsenicals and the Natural Polyarsenic Compound Arsenicin A". Chemistry - A European Journal. 14 (33): 10445–52. doi:10.1002/chem.200801272. PMID 18846604.
- ^ Guella, Graziano; Mancini, Ines; Mariotto, Gino; Rossi, Barbara; Viliani, Gabriele (2009). "Vibrational analysis as a powerful tool in structure elucidation of polyarsenicals: a DFT-based investigation of arsenicin A". Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 11 (14): 2420–2427. doi:10.1039/b816729j. PMID 19325974.
- ^ Di Lu, A. David Rae, Geoff Salem, Michelle L. Weir, Anthony C. Willis and S. Bruce Wild (2010). "Arsenicin A, A Natural Polyarsenical: Synthesis and Crystal Structure". Organometallics. 29 (1): 32–33. doi:10.1021/om900998q.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)