Azo coupling
An azo coupling is an organic reaction between a diazonium compound and another aromatic compound that produces an azo compound. In this electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the aryldiazonium cation is the electrophile and the activated arene is a nucleophile.[1] In most cases, including the examples below, the diazonium compound is also aromatic.
Diazotization
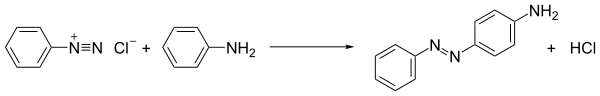
The process of conversion of primary aromatic amines into its diazonium salt is called diazotization. Diazonium salts are important synthetic intermediates that can undergo coupling reactions to form azo dyes and electrophilic substitution reactions to introduce functional groups.
Uses of the reaction
The product will absorb longer wavelengths of light (specifically they absorb in the visible region) than the reactants because of increased conjugation. Consequently, aromatic azo compounds tend to be brightly colored due to the extended conjugated systems. Many are used as dyes (see azo dye).[2] Important azo dyes include methyl red and pigment red 170.
Azo coupling is also used to produce prontosil and other sulfa drugs.
Examples of coupling reactions
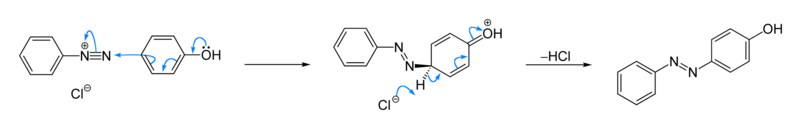
Many procedures have been described.[3][4] Phenol reacts with benzenediazonium chloride to give a yellow-orange azo compound. The reaction is base-catalysed.[2]
The related dye called aniline yellow is produced from the reaction of aniline and the diazonium salt.[2]
Naphthols are popular acceptors. One example is the synthesis of the dye "organol brown" from aniline and 1-naphthol:
Similarly β-naphthol couples with phenyldiazonium electrophile to produce an intense orange-red dye.
References
- ^ Smith, Michael B.; March, Jerry (2007), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (6th ed.), New York: Wiley-Interscience, ISBN 978-0-471-72091-1
- ^ a b c Klaus Hunger; Peter Mischke; Wolfgang Rieper; Roderich Raue; Klaus Kunde; Aloys Engel (2005). "Azo Dyes". Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_245..
- ^ J. L. Hartwell and Louis F. Fieser. "Coupling of o-tolidine and Chicago acid". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 2, p. 145.
- ^ H. T. Clarke and W. R. Kirner. "Methyl red". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 1, p. 374.