Benzodioxan
Appearance

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,3-Dihydro-1,4-benzodioxine
| |
| Other names
Dihydrobenzodioxin; 1,4-Benzodioxane; Benzo-1,4-dioxane; Ethylene o-phenylene dioxide; Pyrocatechol ethylene ether
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 136.150 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
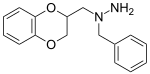
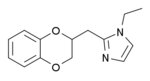
The benzodioxans are a group of isomeric chemical compounds with the molecular formula C8H8O2. There are three isomers of benzodioxan, as the second atom of oxygen of the dioxane can be in a second, third or fourth position : 1,2-dioxane, 1,3-dioxane and 1,4-dioxane, which respectively give 1,2-benzodioxan, 1,3-benzodioxan and 1,4-benzodioxan.
Derivatives
Some derivatives of 1,4-benzodioxan are used as pharmaceuticals including: