Benzopyran
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| ChemSpider | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H7O | |
| Molar mass | 131.154 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
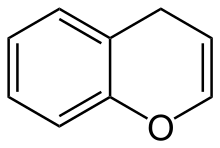
Benzopyran is an polycyclic organic compound that results from the fusion of a benzene ring to a heterocyclic pyran ring. According to IUPAC nomenclature it is called chromene. There are two isomers of benzopyran that vary by the orientation of the fusion of the two rings compared to the oxygen, resulting in 1-benzopyran (chromene) and 2-benzopyran (isochromene)—the number denotes where the oxygen atom is located by standard naphthalene-like nomenclature.
The radical form of benzopyran is paramagnetic. The unpaired electron is delocalized over the whole benzopyran molecule, rendering it less reactive than one would expect otherwise, a similar example is the cyclopentadienyl radical. Commonly, benzopyran is encountered in the reduced state, where it is partially saturated with one hydrogen, introducing a tetrahedral CH2 group in the pyran ring. There are thus many different structural isomers due to multiple possible positions of the oxygen atom and the tetrahedral carbon:
 2H-chromene (2H-1-benzopyran) |
 4H-chromene (4H-1-benzopyran) |
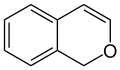 1H-isochromene (1H-2-benzopyran) |
 3H-isochromene (3H-2-benzopyran) |
See also
References
