Caval opening
| Caval opening | |
|---|---|
 The diaphragm. Under surface. (Vena caval foramen labeled near top center, in white region.) | |
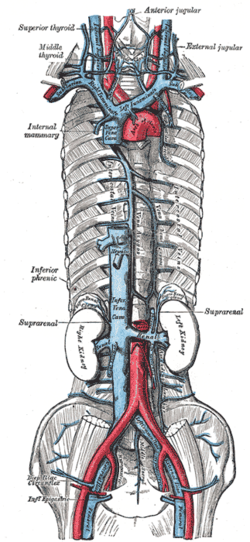 Superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, azygos vein and their tributaries. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | foramen venae cavae |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The caval opening (also vena caval foramen) is a hiatus in the diaphragm of humans through which passes the inferior vena cava, the wall of which is adherent to the margins of the opening, and some branches of the right phrenic nerve.
It is located approximately at the level of the eighth thoracic vertebra (T8), and passes through the diaphragm's central tendon. It is quadrilateral in form, and is placed at the junction of the right and middle leaflets of the central tendon, so that its margins are tendinous.
By being situated in the tendinous part of the diaphragm, it is stretched open every time inspiration occurs. However there has been argument that caval opening actually constricts during inspiration.
Since thoracic pressure decreases upon inspiration and draws the caval blood upwards toward the right atrium, increasing the size of the opening allows more blood to return to the heart, maximizing the efficacy of lowered thoracic pressure returning blood to the heart.
External links
- Template:EMedicineDictionary
- Anatomy photo:40:08-0101 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Major Openings in the Diaphragm"
