Corpus separatum (Jerusalem)
Corpus separatum (Latin for "separated body") is a term used to describe the Jerusalem area in the 1947 United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine. According to the plan the city would be placed under international regime, conferring it a special status due to its shared religious importance. The corpus separatum was one of the main issues of the Lausanne Conference of 1949, besides the other borders and the question of the right of return of Palestinian refugees. The plan was adopted by the General Assembly with a two-thirds majority, although its implementation failed and nowadays the view that Jerusalem should be the capital of both Israel and Palestine is widely supported internationally.[1][2]
Background
With its many holy places and its association with three world religions, Jerusalem had international importance. The United Nations wanted to preserve this status after termination of the British Mandate and guarantee its accessibility. Therefore, the General Assembly proposed a corpus separatum, as described in Resolution 181. It was to be "under a special international regime and shall be administered by the United Nations". The administering body would be the United Nations Trusteeship Council, one of the five UN "Charter" organs. (See Resolution 181, Part III (A).))
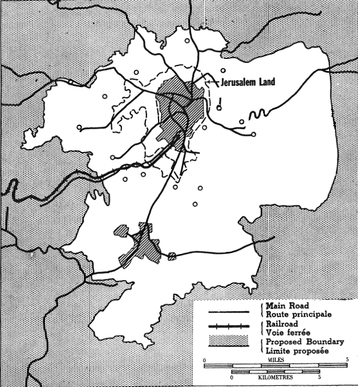
The corpus separatum covered a rather wide area. The Arabs actually wanted to restore the former status as an open city under Arab sovereignty, but eventually supported the corpus separatum.[3] Israel rejected the plan and supported merely a limited international regime.[4][5] In May 1948, Israel told the Security Council that it regarded Jerusalem outside its territory,[6] but now it claimed sovereignty over Jerusalem except the Holy Places.[citation needed]
The corpus separatum in Resolutions 181 and 194
| Jerusalem Corpus Separatum |
|---|
The plan was initially proposed in UN General Assembly Resolution 181 (II) of 29 November 1947. It provided that "Independent Arab and Jewish States and the Special International Regime for the City of Jerusalem ... shall come into existence in Palestine two months after the evacuation of the armed forces of the mandatory Power has been completed but in any case not later than 1 October 1948". All the residents would automatically become "citizens of the City of Jerusalem", unless they would opt for citizenship of the Arab or Jewish State.
As implementation of the partition plan failed due to the Arab-Israeli conflict, Resolution 194 of 11 December 1948 established a Conciliation Commission. Its task was, inter alia, to implement the international regime for the Jerusalem area.
Resolution 194 provided the following directives in the articles 7, 8 and 9:
- [Principle of United Nations supervision]
-
- Resolves that the Holy Places...in Palestine should be protected and free access to them assured,...; that arrangements to this end should be under effective United Nations supervision; ...in presenting...its detailed proposals for a permanent international regime for the territory of Jerusalem, should include recommendations concerning the Holy Places in that territory;...
- [Area and sovereignty]
-
- Resolves that, in view of its association with three world religions, the Jerusalem area, including the present municipality of Jerusalem plus the surrounding villages and towns, the most Eastern of which shall be Abu Dis; the most Southern, Bethlehem; the most Western, Ein Karim (including also the built-up area of Motsa); and the most Northern, Shu'fat, should be accorded special and separate treatment from the rest of Palestine and should be placed under effective United Nations control (this area equals that of Resolution 181, Part III (B));
- [Demilitarization]
-
- Requests the Security Council to take further steps to ensure the demilitarization of Jerusalem at the earliest possible date;
- [Separate control]
-
- Instructs the Conciliation Commission to present to the fourth regular session of the General Assembly detailed proposals for a permanent international regime for the Jerusalem area which will provide for the maximum local autonomy for distinctive groups consistent with the special international status of the Jerusalem area;
- [United Nations Coordinator]
-
- The Conciliation Commission is authorized to appoint a United Nations representative who shall cooperate with the local authorities with respect to the interim administration of the Jerusalem area;
- [Access]
-
- Resolves that, pending agreement on more detailed arrangements among the Governments and authorities concerned, the freest possible access to Jerusalem by road, rail or air should be accorded to all inhabitants of Palestine;
- [Attempts to impede right of access]
-
- Instructs the Conciliation Commission to report immediately to the Security Council, for appropriate action by that organ, any attempt by any party to impede such access;
Further elaboration
On 27 August 1949, the Committee on Jerusalem presented the draft-text of a plan for implementation of the international regime. The plan envisioned a demilitarised Jerusalem divided into a Jewish and an Arab zone, without affecting the nationality of its residents. The commentary notices that the Committee had abandoned the original principle of a corpus separatum. Jerusalem would be the capital of neither Israel nor the Arab state.[7] On 1 September 1949, the Conciliation Commission, chaired by the United States of America, submitted the plan to the General Assembly.[8] The General Assembly did not accept the plan and it was not discussed.[9]
On 5 December 1949, Ben Gurion declared Jewish Jerusalem part of the State of Israel.[10] Four days later, the General Assembly reaffirmed its intention to place Jerusalem under a permanent international regime as a corpus separatum in accordance with the 1947 UN Partition plan by Resolution 303 of 9 December 1949. The resolution requested the Trusteeship Council to complete the preparation of the Statute of Jerusalem without delay.[11]
On 4 April 1950, the Trusteeship Council approved a draft statute for the City of Jerusalem, which was submitted to the General Assembly on 14 June 1950.[12] The statute conformed to the partition plan of 29 November 1947. It could not, however, be implemented.
Failure of the plan
The Partition Plan was not implemented on the ground, as war broke out between six Arab nations and the newly declared State of Israel. Months of fierce fighting ended with Israel in control of west Jerusalem and Jordan controlling the east. On 2 August 1948 the government of Israel declared the Israeli-controlled part of the Jerusalem area Israel-occupied territory.[13] At the end of the 1948-49 War, under the Armistice Agreement, an Armistice Demarcation Line was drawn, with Western Jerusalem occupied by Israel and the whole West Bank occupied by Transjordan. By letter of 31 May 1949, Israel told the UN Committee on Jerusalem that it considered another attempt to implement a united Jerusalem under international regime "impracticable" and favored an alternative UN scenario in which Jerusalem would be divided into a Jewish and an Arab zone.[4] Israeli Prime Minister Ben-Gurion declared "Jewish Jerusalem" (West Jerusalem) an organic, inseparable part of the State of Israel on 5 December 1949. He also declared Israel no longer bound by Resolution 181 and the corpus separatum null and void, on grounds that the UN had not made good on its guarantees of security for the people of Jerusalem under that agreement.[10]
Following the Six-Day War of 1967, Israel also gained military control of East Jerusalem[14] and the West Bank. Israel expanded the municipal boundaries of occupied Jerusalem; these, however, are not recognized internationally. The present municipal boundaries of Jerusalem are not the same as those of the corpus separatum set out in the Partition Plan and do not include Bethlehem, Motza, or Abu Dis.
International support
As the UN has never revoked its resolutions 181 and 194, it maintains the official position that Jerusalem should be placed under a special international regime.[15] Nevertheless, Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon said on 28 October 2009 that Jerusalem must be the capital of both Israel and Palestine.[16]
European Union
The European Union continues to support the internationalisation of Jerusalem in accordance with the 1947 UN Partition Plan and regards Jerusalem as having the status of corpus separatum.[17][dead link]
United States
The USA has never officially relinquished its early support of the corpus separatum. On 23 October 1995, the Congress passed the advisory Jerusalem Embassy Act saying that "Jerusalem should be recognized as the capital of the State of Israel; and the United States Embassy in Israel should be established in Jerusalem no later than May 31, 1999". Since 1998, the congressional suggestion to relocate the embassy from Tel Aviv has been suspended semi-annually by every sitting President, each time stating that this "is necessary to protect the national security interests of the United States". Since the U.S. Congress does not control U.S. foreign policy, despite the Embassy Act, official U.S. documents and web sites do not refer to Jerusalem as the capital of Israel.[18]
Holy See
The Holy See has previously expressed support for the status of corpus separatum. Pope Pius XII was the among the first to make such a proposal in the 1949 encyclical Redemptoris nostri cruciatus. This idea was later re-proposed during the papacies of John XXIII, Paul VI and John Paul II.
Status after 1967

The Israeli Knesset passed a Jerusalem Law declaring united Jerusalem to be Israel's capital in 1980, although the clause "the integrity and unity of greater Jerusalem (Yerushalayim rabati) in its boundaries after the Six-Day War shall not be violated" was dropped from the original bill. United Nations Security Council Resolution 478 of 20 August 1980 condemned this and no countries have located their embassies in Jerusalem.[19]
In numerous resolutions, the UN has declared every action changing the status of Jerusalem illegal and therefore null and void and having no validity. A recent such resolution was Resolution 66/18 of 30 November 2011.[15]
See also
- Positions on Jerusalem
- UN General Assembly Resolution 194, (1948)
- United Nations Conciliation Commission, (1949)
References
- ^ UNGA, 29 November 2012 Resolution 67/19. Status of Palestine in the United Nations (doc.nr. A/RES/67/19 d.d. 04-12-2012)
- ^ European Parliament, 5 July 2012, Resolution 2012/2694(RSP)
- ^ UN Committee on Jerusalem, Meeting between the Committee on Jerusalem and the delegations of the Arab states, 20 June 1949[permanent dead link] (doc.nr. A/AC.25/Com.Jer./SR.33)
- ^ a b Letter dated 31 May 1949, addressed by Mr. Walter Eytan, Head of the Delegation of Israel[permanent dead link] (doc.nr. A/AC.25/Com.Jer/9 d.d. 01-06-1949)
- ^ UNCCP, 5 April 1949, second progress report Archived 2013-06-17 at the Wayback Machine (doc.nr. A/838 d.d.19-04-1949), see par. 28.
- ^ UNGA, 22 May 1948, Replies of Provisional Government of Israel to Security Council questionnaire Archived 2013-05-28 at the Wayback Machine (doc.nr. S/766)
- ^ UN Committee on Jerusalem, 27 August 1949, Third progress report to the United Nations Conciliation Commission for Palestine[permanent dead link] (doc.nr. A/AC.25/Com.Jer/12)
- ^ UNCCP, 1 September 1949 Palestine - Proposals for a permanent international regime for the Jerusalem area[permanent dead link] (doc.nr. A/973 d.d. 12-09-1949). The plan was explained in document A/973/Add.1[permanent dead link] (12-11-1949).
- ^ CEIRPP/DPR, 1 January 1981, The status of Jerusalem Archived 2012-12-08 at the Wayback Machine, see chapter VI
- ^ a b Knesset website, Statements of the Prime Minister David Ben-Gurion Regarding Moving the Capital of Israel to Jerusalem. Retrieved 13-05-2013
- ^ UNGA, 9 December 1949, Resolution 303 (IV). Palestine: Question of an international regime for the Jerusalem area and the protection of the Holy Places Archived 2014-10-16 at the Wayback Machine [doc.nr. A/RES/303 (IV)]
- ^ UNGA, 14 June 1950, General Assembly official records: Fifth session supplement no. 9 (A/1286) Archived 2012-11-04 at the Wayback Machine, Question of an international regime for the Jerusalem area and protection of the Holy Places – Special Report of the Trusteeship Council (see Annex II)
- ^ Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs, 12 August 1948, 2 Jerusalem Declared Israel-Occupied City- Government Proclamation (onweb.archive.org/)
- ^ Dumper, The politics of Jerusalem since 1967, Page 42: "Despite full military control and the assertion of total Israeli sovereignty over the whole of Jerusalem"
- ^ a b UNGA, 30 November 2011, Resolution adopted by the General Assembly, 66/18. Jerusalem (doc.nr. A/RES/66/18 d.d. 26-01-2012)
"Recalling its resolution 181 (II) of 29 November 1947, in particular its provisions regarding the City of Jerusalem,"
"Reiterates its determination that any actions taken by Israel, the occupying Power, to impose its laws, jurisdiction and administration on the Holy City of Jerusalem are illegal and therefore null and void and have no validity whatsoever," - ^ Jerusalem must be capital of both Israel and Palestine, Ban says, UN News Centre, (October 28, 2009)
- ^ Foundation for Middle East Peace – May 1999: "Europe Affirms Support for a Corpus Separatum for Greater Jerusalem"
- ^ Adam Kredo, Solving the White House photo mystery over ‘Jerusalem, Israel’. JTA, 16 August 2011
- ^ Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Resident Missions – Heads of Missions and Addresses. 2016. [1]