Cotton gin


A cotton gin is a machine that quickly and easily separates cotton fibers from their seeds, allowing for much greater productivity than manual cotton separation.[2] The fibers are processed into clothing or other cotton goods, and any undamaged cotton was used for clothes. Seeds may be used to grow more cotton or to produce cottonseed oil and meal.
Although simple handheld roller gins have been used in India and other countries since at least 500 AD,[3] the first modern mechanical cotton gin was created by American inventor Eli Whitney in 1793 and patented in 1794. However, the Indian worm-gear roller gin, invented some time around the sixteenth century,[4] has, according to Lakwete, remained virtually unchanged up to the present time. Whitney's gin used a combination of a wire screen and small wire hooks to pull the cotton through, while brushes continuously removed the loose cotton lint to prevent jams. It revolutionized the cotton industry in the United States, but also led to the growth of slavery in the American South as the demand for cotton workers rapidly increased. The invention has thus been identified as an inadvertent contributing factor to the outbreak of the American Civil War.[5] Modern automated cotton gins use multiple powered cleaning cylinders and saws, and offer far higher productivity than their hand-powered forebears.[6]
History
Purpose
Cotton fibers are produced in the seed pods ("bolls") of the cotton plant where the fibers ("lint") in the bolls are tightly interwoven with seeds. To make the fibers usable, the seeds and fibers must first be separated, a task which had been previously performed manually, with production of cotton requiring hundreds of hours of labor for the separation. Many simple seed-removing devices had been invented, but until the innovation of the cotton gin, most required significant operator attention and worked only on a small scale.[7]
Early cotton gins
The earliest versions of the cotton gin consisted of a single roller made of iron or wood and a flat piece of stone or wood. Evidence for this type of gin has been found in Africa, Asia, and North America. The first documentation of the cotton gin by contemporary scholars is found in the fifth century A.D., in the form of Buddhist paintings depicting a single-roller gin in the Ajanta Caves in western India.[3] These early gins were difficult to use and required a great deal of skill. A narrow single roller was necessary to expel the seeds from the cotton without crushing the seeds. The design was similar to that of a metate, which was used to grind grain. The early history of the cotton gin is ambiguous, because archeologists likely mistook the cotton gin's parts for other tools.[3]
Between the 12th and 14th centuries, dual-roller gins appeared in India and China. The Indian version of the dual-roller gin was prevalent throughout the Mediterranean cotton trade by the 16th century. This mechanical device was, in some areas, driven by water power.[8]
Eli Whitney's patent
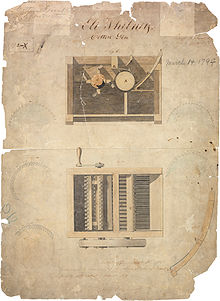
The modern mechanical cotton gin was invented in the United States of America in 1793 by Eli Whitney (1765–1825). Whitney applied for a patent on October 28, 1793; the patent was granted on March 14, 1794, but was not validated until 1807. Whitney's patent was assigned patent number 72X.[9] There is slight controversy over whether the idea of the modern cotton gin and its constituent elements are correctly attributed to Eli Whitney. The popular image of Whitney inventing the cotton gin is attributed to an article on the subject written in the early 1870s and later reprinted in 1910 in The Library of Southern Literature. In this article, the author claimed Catherine Littlefield Greene suggested to Whitney the use of a brush-like component instrumental in separating out the seeds and cotton. To date, Greene's role in the invention of the gin has not been verified independently.[10]
Whitney's cotton gin model was capable of cleaning 50 pounds (23 kg) of lint per day. The model consisted of a wooden cylinder surrounded by rows of slender spikes, which pulled the lint through the bars of a comb-like grid.[11] The grids were closely spaced, preventing the seeds from passing through. Loose cotton was brushed off, preventing the mechanism from jamming.
Many contemporary inventors attempted to develop a design that would process short staple cotton, and Hodgen Holmes, Robert Watkins, William Longstreet, and John Murray had all been issued patents for improvements to the cotton gin by 1796.[12] However, the evidence indicates Whitney did invent the saw gin, for which he is famous. Although he spent many years in court attempting to enforce his patent against planters who made unauthorized copies, a change in patent law ultimately made his claim legally enforceable – too late for him to make much money from the device in the single year remaining before the patent expired.[13]
Effects in the United States
Prior to the introduction of the mechanical cotton gin, cotton had required considerable labor to clean and separate the fibers from the seeds.[14] With Eli Whitney’s introduction of "teeth" in his cotton gin to comb out the cotton and separate the seeds, cotton became a tremendously profitable business, creating many fortunes in the Antebellum South. New Orleans, Mobile, Charleston and Galveston became major shipping ports, deriving substantial economic benefit from cotton raised throughout the South. Additionally, the greatly expanded supply of cotton created strong demand for textile machinery and improved machine designs that replaced wooden parts with metal. This led to the invention of many machine tools in the early 19th century.[2]
The invention of the cotton gin caused massive growth in the production of cotton in the United States, concentrated mostly in the South. Cotton production expanded from 750,000 bales in 1830 to 2.85 million bales in 1850. As a result, the region became even more dependent on plantations and slavery, with plantation agriculture becoming the largest sector of its economy.[15] While it took a single slave about ten hours to separate a single pound of fiber from the seeds, a team of two or three slaves using a cotton gin could produce around fifty pounds of cotton in just one day.[16] The number of slaves rose in concert with the increase in cotton production, increasing from around 700,000 in 1790 to around 3.2 million in 1850.[17] By 1860, black slave labor from the American South was providing two-thirds of the world’s supply of cotton, and up to 80% of the crucial British market.[18] The cotton gin thus “transformed cotton as a crop and the American South into the globe's first agricultural powerhouse, and – according to many historians – was the start of the Industrial Revolution".[19]

According to the Eli Whitney Museum website:
Whitney (who died in 1825) could not have foreseen the ways in which his invention would change society for the worse. The most significant of these was the growth of slavery. While it was true that the cotton gin reduced the labor of removing seeds, it did not reduce the need for slaves to grow and pick the cotton. In fact, the opposite occurred. Cotton growing became so profitable for the planters that it greatly increased their demand for both land and slave labor. In 1790 there were six slave states; in 1860 there were 15. From 1790 until Congress banned the importation of slaves from Africa in 1808, Southerners imported 80,000 Africans. By 1860 approximately one in three Southerners was a slave.[20]
Because of its inadvertent effect on American slavery, and on its ensuring that the South's economy developed in the direction of plantation-based agriculture (while encouraging the growth of the textile industry elsewhere, such as in the North), the invention of the cotton gin is frequently cited as one of the indirect causes of the American Civil War.[5][21][22]
Modern cotton gins


In modern cotton production, cotton arrives at industrial cotton gins either in trailers or in compressed "modules", which weigh up to 10 metric tons each. Cotton arriving in trailers is sucked into the gin via a pipe, approximately 16 inches (41 cm) in diameter, that is swung over the cotton. This pipe is usually manually operated, but is increasingly automated in modern cotton plants. The need for trailers to haul the product to the gin has been drastically reduced since the introduction of the module. If the cotton is shipped in modules, the module feeder breaks the modules apart using spiked rollers and extracts the largest pieces of foreign material from the cotton. The module feeder's loose cotton is then sucked into the same starting point as the trailer cotton.
The cotton then enters a dryer, which removes excess moisture. The cylinder cleaner uses six or seven rotating, spiked cylinders to break up large clumps of cotton. Finer foreign material, such as soil and leaves, passes through rods or screens for removal. The stick machine uses centrifugal force to remove larger foreign matter, such as sticks and burrs, while the cotton is held by rapidly rotating saw cylinders.
The gin stand uses the teeth of rotating saws to pull the cotton through a series of "ginning ribs", which pull the fibers from the seeds which are too large to pass through the ribs. The cleaned seed is then removed from the gin via an auger conveyor system. The seed is reused for planting or is sent to an oil mill to be further processed into cottonseed oil and cottonseed meal. The lint cleaners again use saws and grid bars, this time to separate immature seeds and any remaining foreign matter from the fibers. The bale press then compresses the cotton into bales for storage and shipping. Modern gins can process up to 15 tonnes (33,000 lb) of cotton per hour.[6]
References
- ^ Lakwete, 182.
- ^ a b Roe, Joseph Wickham (1916), English and American Tool Builders, New Haven, Connecticut: Yale University Press, LCCN 16011753. Reprinted by McGraw-Hill, New York and London, 1926 (LCCN 27-24075); and by Lindsay Publications, Inc., Bradley, Illinois, (ISBN 978-0-917914-73-7).
- ^ a b c Lakwete, 1–6.
- ^ https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=K8kO4J3mXUAC&pg=PA53&lpg=PA53&dq=Worm-Gear+Gin+India&source=bl&ots=5BkhW9ZBsQ&sig=J4OAypTaUv3Tu7nZMsk0Y9Yhqvo&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiq4p_85ubLAhUJuBoKHQnsDyUQ6AEIcDAR#v=onepage&q=Worm-Gear%20Gin%20India&f=false
- ^ a b Kelly, Martin. "Top Five Causes of the Civil War: Leading up to Secession and the Civil War". About.com. Retrieved March 14, 2011.
- ^ a b inventors.about.com; "Background on the Cotton Gin", retrieved October 22, 2010.
- ^ Bellis, Mary. inventors.about.com; "The Cotton Gin and Eli Whitney", retrieved March 12, 2012.
- ^ Baber, Zaheer (1996). The Science of Empire: Scientific Knowledge, Civilization, and Colonial Rule in India. Albany: State University of New York Press. p. 57. ISBN 0-7914-2919-9.
- ^ http://inventors.about.com/od/cstartinventions/ss/patent_X72.htm
- ^ "Catherine Littlefield Greene, Brain Behind the Cotton Gin". Finding Dulcinea. March 4, 2010. Retrieved November 6, 2013.
- ^ Harr, M. E. (1977). Mechanics of particulate media: A probabilistic approach. McGraw-Hill.
- ^ Lakwete, 64–76.
- ^ The American Historical Review by Henry Eldridge Bourne, Robert Livingston Schuyler Editors: 1895 – July 1928; J.F. Jameson and others.; Oct. 1928–Apr. 1936, H.E. Bourne and others; July 1936–Apr. 1941, R.L. Schuyler and others; July 1941– G.S. Ford and others. Published 1991, American Historical Association [etc.], pp 90–101.
- ^ Hamner, Christopher. teachinghistory.org, "The Disaster of Innovation", retrieved July 11, 2011.
- ^ Pierson, Parke (September 2009). "Seeds of conflict". America's Civil War. 22 (4): 25.
- ^ Woods, Robert (September 1, 2009). “A Turn of the Crank Started the Civil War." Mechanical Engineering.
- ^ Smith, N. Jeremy (July 2009). "Making Cotton King". World Trade. 22 (7): 82.
- ^ "Cotton – a history". New Internationalist. 399: 18–19. April 2007.
- ^ Underhill, Paco (2008). "The cotton gin, oil, robots and the store of 2020". Display & Design Ideas. 20 (10): 48.
- ^ eliwhitney.org, The Cotton Gin – Eli Whitney Museum and Workshop. Retrieved November 23, 2011.
- ^ Joe Ryan. "What Caused the American Civil War?" AmericanCivilWar.com. Retrieved March 14, 2011.
- ^ Randy Golden, "Causes of the Civil War". About North Georgia. Retrieved March 14, 2011.
Bibliography
- Lakwete, Angela (2003). Inventing the Cotton Gin: Machine and Myth in Antebellum America. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 9780801873942.
External links
- Overview of a Cotton Gin – USDA site
- The Story of Cotton – National Cotton Council of America site
- National Cotton Ginners Association
- US Cotton Gin Industry – EH.Net Encyclopedia of Economic History
- Invention of Cotton Gin – eHistory.com
- Cotton: the fiber of life – includes a schematic diagram illustrating the seed removal process
- Video of manual cotton gin in operation via YouTube
