Dado (architecture)
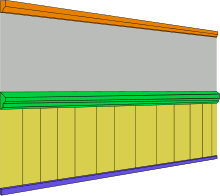
In architecture, the dado is the lower part of a wall,[1] below the dado rail and above the skirting board. The word is borrowed from Italian meaning "die" (as an architectural term) or plinth.
Decorative treatment
This area is given a decorative treatment different from that for the upper part of the wall; for example panelling, wainscoting or lincrusta. The purpose of the dado treatment to a wall is both aesthetic and functional. Historically, the panelling below the dado rail was installed to cover the lower part of the wall which was subject to stains associated with rising damp; additionally it provided protection from furniture and passing traffic. The dado rail itself is sometimes referred to misleadingly as a chair rail, though its function is principally aesthetic and not to protect the wall from chair backs.
Derivation
The name derives from the architectural term for the part of a pedestal between the base and the cornice.
Gallery
-
Dado in carved oak, designed by W.S. Barber at Spring Hall, Halifax
See also
References
- ^ "Dado - definition". Merriam-Webster. Retrieved March 10, 2013.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help)

