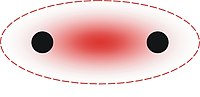
Delta bond


In chemistry, delta bonds (δ bonds) are covalent chemical bonds, where four lobes of one involved atomic orbital overlap four lobes of the other involved atomic orbital. This overlap leads to the formation of a bonding molecular orbital with two nodal planes which contain the internuclear axis and go through both atoms.[1][2][3][4]
The Greek letter δ in their name refers to d orbitals, since the orbital symmetry of the delta bond is the same as that of the usual (4-lobed) type of d orbital when seen down the bond axis. This type of bonding is observed in atoms that have occupied d orbitals with low enough energy to participate in covalent bonding, for example, in organometallic species of transition metals. Some rhenium, molybdenum and chromium compounds contain a quadruple bond, consisting of one sigma bond, two pi bonds and one delta bond.
The orbital symmetry of the delta bonding orbital is different from that of a pi antibonding orbital, which has one nodal plane containing the internuclear axis and a second nodal plane perpendicular to this axis between the atoms.
The delta notation was introduced by Robert Mulliken in 1931.[5][6] The first compound identified as having a delta bond was potassium octachlorodirhenate(III). In 1965, F.A. Cotton reported that there was delta-bonding as part of the rhenium–rhenium quadruple bond in the [Re2Cl8]2− ion.[7]
References
- ^ F.A. Cotton and G. Wilkinson, "Advanced Inorganic Chemistry" (5th edn, John Wiley 1988), p. 1087–1091
- ^ B. Douglas, D.H. McDaniel and J.J. Alexander, "Concepts and Models of Inorganic Chemistry" (2nd edn, Wiley 1983), p. 137
- ^ J.E. Huheey, "Inorganic Chemistry" (3d edn, Harper and Row 1983). p. 743-744
- ^ G.L. Miessler and D.A. Tarr, "Inorganic Chemistry" (2nd edn, Prentice-Hall 1999), p. 123-124
- ^ The Origin of the Sigma, Pi, Delta Notation for Chemical Bonds William B. Jensen Journal of Chemical Education 2013 90 (6), 802–803 doi:10.1021/ed200298h
- ^ Bonding Power of Electrons and Theory of Valence. Robert S. Mulliken Chemical Reviews 1931 9 (3), 347–388 doi:10.1021/cr60034a001
- ^ Metal-Metal Bonding in [Re2X8]2− Ions and Other Metal Atom Clusters F. A. Cotton Inorganic Chemistry 1965 4 (3), 334–336 doi:10.1021/ic50025a016