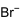Dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide
|
| ||||
| Names | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide
| ||||
| Other names
Distearyldimethylammonium bromide
| ||||
| Identifiers | ||||
3D model (JSmol)
|
||||
| ||||
| ||||
| Properties | ||||
| C38H80BrN | ||||
| Molar mass | 630.969 g·mol−1 | |||
| Appearance | White solid | |||
| Hazards | ||||
| GHS labelling: | ||||
| class="wikitable collapsible" style="min-width: 50em;" | ||||
| Pictogram | Code | Symbol description | Image link | |
 |
GHS01 | {{GHS exploding bomb}} | Image:GHS-pictogram-explos.svg | Explosive |
 |
GHS02 | {{GHS flame}} | Image:GHS-pictogram-flamme.svg | |
 |
GHS03 | {{GHS flame over circle}} | Image:GHS-pictogram-rondflam.svg | |
 |
GHS04 | {{GHS gas cylinder}} | Image:GHS-pictogram-bottle.svg | |
 |
GHS05 | {{GHS corrosion}} | Image:GHS-pictogram-acid.svg | Corrosive |
 |
GHS06 | {{GHS skull and crossbones}} | Image:GHS-pictogram-skull.svg | Accute Toxic |
 |
GHS07 | {{GHS exclamation mark}} | Image:GHS-pictogram-exclam.svg | Irritant |
 |
GHS08 | {{GHS health hazard}} | Image:GHS-pictogram-silhouette.svg | Health Hazard |
 |
GHS09 | {{GHS environment}} | Image:GHS-pictogram-pollu.svg | Environment |
See also
- {{H-phrases}}
- {{P-phrases}}
- Category:GHS templates
|-
|-
| style="padding-left:1em;" |
| Warning[1]
|-
|-
| style="padding-left:1em;" |
| H315, H319, H335[1]
|-
|-
| style="padding-left:1em;" |
| P261, P305+P351+P338, P310[1]
|-
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | [1] |-
| colspan=2 style="text-align:left; background:#f8eaba; border:1px solid #a2a9b1;" |
|-
|}
Dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide (also dioctadecyldimethylammonium bromide or DODAB) is a double-chained quaternary ammonium surfactant that forms unilamellar vesicles (ULVs) in water. Among various preparation methods, the ‘‘hot-water” method offers a simple procedure to prepare DODAB cationic vesicles by simply dissolving the DODAB in hot water above 50 °C, i.e., chain melting (main) transition, Tm. In general, the DSC thermograms of the unsonicated DODAB dispersions are dominated by two endotherms; the pre- (35–36 °C) and main transition (42.7–45 °C) peaks. Moreover, in literature reported the presence of a third endotherm (post transition) at 52.2 °C. The main transition (Tm) is ascribed to gel to liquid-crystalline phase transition in which the alkyl chains transform from solidlike to liquid-like state.
The 10 mM DODAB is a critical concentration, below which the dispersions consist of large polydispersed unilamellar vesicles (ULVs) that exhibit a local (chain melting) transition at 43 °C, beyond which a structural transition occurs: ULVs --> MLVs (multilamellar vesicles) as indicated by the sudden increase in the dynamic moduli. However, above 10 mM DODAB, the dispersions are mostly formed by ULVs in coexistence with lamellar fragments resulting in a network that shows a rheogram similar to that of hexagonal liquid-crystalline phase. [3]
See also
- Dimethyldioctadecylammonium chloride
- cetyl trimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) a.k.a. hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide,
- cetyl trimethylammonium chloride (CTAC);
References
- ^ a b c d Sigma-Aldrich Co., Dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide. Retrieved on 2016-10-25.
- ^ "Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals" (pdf). 2021. Annex 3: Codification of Statements and Pictograms (pp 268–385).
- ^ Coppola L. , Youssry M. , Nicotera I. , Gentile L. , " Rheological investigation of thermal transitions in vesicular dispersion". Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2009, Vol. 338, n. 2, pp. 550-557. Abstract