Dithiolane
Appearance
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Dithiolane
| |||
| Other names
1,2-dithiolane, 1,3-dithiolane
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H6S2 | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
1,2-Ethanedithiol | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
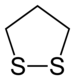
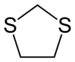
A dithiolane is a sulfur heterocycle derived from cyclopentane by replacing two methylene bridges (-CH
2- units) with thioether groups. The parent compounds are 1,2-dithiolane and 1,3-dithiolane.
1,2-Dithiolanes, such as lipoic acid, are cyclic disulfides.
1,3-Dithiolanes are important as protecting groups for carbonyl compounds, since they are inert to a wide range of conditions. Reacting a carbonyl group with 1,2-ethanedithiol converts it to a 1,3-dithiolane, as detailed below.

A dithiolanone is a dithiolane which is also a ketone.