Thomas Voigt
Thomas Voigt (June 16, 1787 – August 3, 1844) was an American clockmaker. He apprenticed under his father, Henry Voigt, an American Revolution era clockmaker and inventor.
Early life
[edit]Thomas Voigt was the son of Philadelphians Margaret and Henry Voigt.[1][2]

At an early age, Thomas began an apprenticeship in the watch and clock building portion of his father's business interests. Thomas developed an enthusiastic interest in his father's watch and clock making as a young man, and gradually assumed its lead.
From 1804 to 1809, Thomas assisted his father on a contract received from the trustees of Princeton University to repair war damage to the orrery built by David Rittenhouse and his father in 1771. Thomas and Henry Voigt brought the orrery to their shop in Philadelphia to complete the repairs.
They moved their business from Second Street between Vine and Race Streets to a location across the street from the first US Mint at Philadelphia – 44 North Seventh Street. Thomas married Maria Kessler who was a granddaughter of German emigrants Mary Ritchouer and Leonard Kessler; daughter of Michael Kessler; and niece of Naval Historian John Kessler.[4][5][6]
Astronomical Case Clock
[edit]

Jefferson engaged Voigt to build a tall case clock with advanced time keeping precision that would support his study of lunar and solar cycles. The clock that Voigt would construct for President Jefferson would become known as his Astronomical Case Clock. Voigt completed Jefferson's Astronomical Case Clock in 1812, but due to the War of 1812, was unable to deliver the finished Clock to Jefferson's home, Monticello, until December 1815.
The clock's case was a multi layered polished mahogany structure; its dial decorated with gilt and black lunettes; and its cost ($115.50) was nearly twice the original estimate. Although it was more ornate and more expensive than President Jefferson's original plan, he accepted Thomas's clock and placed the eight-day clock in his private suite of rooms. He used it in his studies until his death on July 4, 1826.
The Astronomical Case Clock measures 94 inches tall, 18 inches wide, and 11 inches deep. The clock was designed for astronomical purposes without a striking mechanism. Its single pendulum and single weight construction operate for eight days without attendance. Jefferson's use of the clock for astronomical studies can be seen from his annotations of the daily weight positions inside the clock.
After Jefferson's death, Robley Dunglison, professor of medicine at the University of Virginia, had attended Thomas Jefferson in the period preceding his death and was presented the Astronomical Case Clock for his medical devotion to President Jefferson in the final period of his life. A small brass plate affixed to the top right rear of the clock's interior reads as follows: “Clock of President Jefferson Gift of daughter Mrs. Randolph to Dr. Rolley Dunglison 1826 ”
The Astronomical Case Clock remained in Dunglison's family until his son, William Ladam Dunglison, donated it to the Historical Society of Pennsylvania in 1894. In 1999, the Thomas Jefferson Foundation with the aid of a private donor purchased The Astronomical Case Clock from the Historical Society of Pennsylvania for an undisclosed sum and returned it to Jefferson's study at Monticello where it stands today.

Ohio Clock
[edit]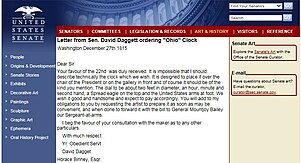



In 1815, the US Senate placed the following order with Thomas Voigt for a clock for its chambers.
In 1816, Voigt delivered the Ohio Clock to the US Senate. The Ohio Clock was positioned within the restored US Capitol in the Senate Chamber. In 1859, when a new Senate chamber was constructed, the Ohio Clock was positioned opposite the main entrance to the new Senate chamber where it resides today.[7]
The name of the clock that Voigt delivered to the US Senate in response to Senator Daggett's order has been a topic of speculation. Its name, the Ohio Clock, has been associated with the seventeen stars and stripes added to the cabinet case by Voigt. Ohio was admitted to the union of US states during the administration of President Jefferson. It may therefore be speculated that Voigt's use of seventeen stars and stripes represented the admission of Ohio to the union during the presidential administration of Jefferson.[original research?]
Legacy
[edit]

Thomas Voigt and his wife Maria Kessler Voigt reside in a plot near his parents and other family members in Laurel Hill Cemetery in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Voigt built many clocks for customers and family members.
References
[edit]This article was initiated by the recollections of Thomas Voigt by his descendants Cynthia Cooper, Hubert Joseph Kessler, and Eleanor Ruth Kessler Whitehead. The authors are also grateful to historian Tim McGrath for supplying the autobiography of John Kessler.[4][5][6] This article was prepared by William B. Kessler Jr., Mary K. Kessler, and William B. Kessler III.
Footnotes
[edit]- ^ History Corner: Henry Voigt Professional Surveyor Archives by Silvio A. Bedini Historian Emeritus with the Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC (Download Here)
- ^ 1. Transit and Equal Altitude Instrument Smithsonian National Museum of American History Behring Center Physical Sciences Collection – Surveying and Geodesy Catalogue number: PH*311772
- ^ a b Painting is on display at today’s Philadelphia Mint, 151 Independence Mall East, Philadelphia, PA 19106
- ^ a b Life of John Kessler an 1823 autobiography by John Kessler on file at the Pennsylvania State Archives, 350 North Street, Harrisburg, PA 17120-0090
- ^ a b McGrath, Tim (2010). John Barry : an American hero in the Age of Sail. Yardley, Pa.: Westholme. ISBN 9781594161049. OCLC 495778699.
- ^ a b McGrath, Tim (2014). Give me a fast ship : the Continental Navy and America's Revolution at sea. New York, New York. ISBN 9780451416100. OCLC 861673685.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Photos and information obtained in an October, 2004 visit to the U. S. Capitol by the author obtained with the assistance of U. S. Senate Historian, Richard Allan Baker
