Elaidinization
Elaidinization is a chemical reaction which alters the orientation of double-bonds from cis- to trans-. It is most often performed on fats and oils to increase both the melting point and the shelf life without reducing the degree of unsaturation. The typical product of elaidinization is trans fat.
Etymology
The word originates from elaidic acid, the trans-isomer of oleic acid.
Reaction
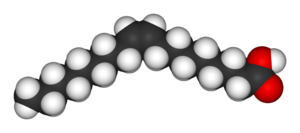
Elaidinization of oleic acid, a common component of vegetable oils, yields its trans-isomer elaidic acid.
| Oleic acid | Elaidic acid |
|---|---|
| Oleic acid is a cis unsaturated fatty acid, a common component of natural vegetable oils. | Elaidic acid is a trans unsaturated fatty acid often created by partial hydrogenation or elaidinisation of vegetable oils. |
 |
 |
 |
|
| These fatty acids are isomers (chemically identical except for the orientation of the double bond). | |

