Favorskii rearrangement
| Favorskii rearrangement | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Alexei Yevgrafovich Favorskii |
| Reaction type | Rearrangement reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| Organic Chemistry Portal | favorsky-reaction |
| RSC ontology ID | RXNO:0000385 |
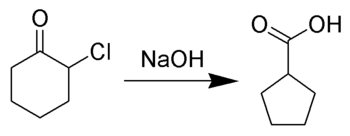
The Favorskii rearrangement is principally a rearrangement of cyclopropanones and α-halo ketones that leads to carboxylic acid derivatives. In the case of cyclic α-halo ketones, the Favorskii rearrangement constitutes a ring contraction. This rearrangement takes place in the presence of a base, sometimes hydroxide, to yield a carboxylic acid, but usually either an alkoxide base or an amine to yield an ester or an amide, respectively. α,α'-Dihaloketones eliminate HX under the reaction conditions to give α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds.[1][2][3][4][5] Note that trihalomethyl ketone substrates will result in haloform and carboxylate formation via the haloform reaction instead.
History
The reaction is named for the Russian chemist Alexei Yevgrafovich Favorskii.[6][7][8]
Reaction mechanism
The reaction mechanism is thought to involve the formation of an enolate on the side of the ketone away from the chlorine atom. This enolate cyclizes to a cyclopropanone intermediate which is then attacked by the hydroxide nucleophile. Its formation can otherwise be viewed as a 2-electron electrocyclization of a 1,3-dipole, which can be captured in Diels Alder reactions. The cyclopropanone intermediate is opened to yield the more stable carbanion, which is quickly protonated.[9]

The second step has also been proposed to be stepwise process, with chloride anion leaving first to produce a zwitterionic oxyallyl cation before a disrotatory electrocyclic ring closure takes place to afford the cyclopropanone intermediate.[10]
Usage of alkoxide anions such as sodium methoxide, instead of sodium hydroxide, yields the ring-contracted ester product.
When enolate formation is impossible, the Favorskii rearrangement takes place by an alternate mechanism, in which addition to hydroxide to the ketone takes place, followed by concerted collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate and migration of the neighboring carbon with displacement of the halide. This is sometimes known as the pseudo-Favorskii rearrangement or quazi-Favorskii rearrangement, although previous to labeling studies, it was thought that all Favorskii rearrangements proceeded through this mechanism.
|
| An animation of the reaction mechanism |
Wallach degradation
In the related Wallach degradation (Otto Wallach, 1918) not one but two halogen atoms flank the ketone resulting in a new contracted ketone after oxidation and decarboxylation[11][12]
Photo-Favorskii reaction
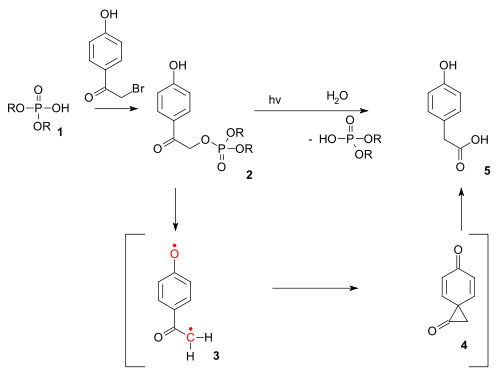
The reaction type also exists as a photochemical reaction. The photo-Favorskii reaction has been used in the photochemical unlocking of certain phosphates (for instance those of ATP) protected by so-called p-hydroxyphenacyl groups.[13] The deprotection proceeds through a triplet diradical (3) and a dione spiro intermediate (4) although the latter has thus far eluded detection.[14]
See also
- Trimethylenemethane cycloaddition, which can proceed via a similar mechanism
- Homo-Favorskii rearrangement, the rearrangement of β-halo ketones and cyclobutanones
References
- ^ Cope, Arthur (1960). Organic Reaction Volume XI (1 ed.). New York: Wiley-Interscience. doi:10.1002/jps.2600500225. ISBN 9780471171270.
- ^ Wohllebe, J.; Garbisch, E. W. (1977). "Ring Contraction via a Favorskii-Type Rearrangement: Cycloundecanone". Organic Syntheses. 56: 107. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.056.0107; Collected Volumes, vol. 6, p. 368.
- ^ Shioiri, Takayuki; Kawai, Nobutaka (1978). "New methods and reagents in organic synthesis. 2. A facile conversion of alkyl aryl ketones to α-arylalkanoic acids using diphenyl phosphorazidate. Its application to a new synthesis of ibuprofen and naproxen, nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents". J. Org. Chem. 43 (14): 2936–2938. doi:10.1021/jo00408a049.
- ^ Hamada, Yasumasa; Shioiri, Takayuki (1982). "Cycloundecanecarboxylic Acid". Organic Syntheses. 62: 191. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.062.0191; Collected Volumes, vol. 7, p. 135.
- ^ Goheen, D. W.; Vaughan, W. R. (1963). "Cyclopentanecarboxylic acid, methyl ester". Organic Syntheses. 39: 37. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.039.0037; Collected Volumes, vol. 4, p. 594.
- ^ Favorskii, A. E. (1894). J. Russ. Phys. Chem. Soc. 26: 590.
{{cite journal}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Favorskii, A. E. (1905). J. Russ. Phys. Chem. Soc. 37: 643.
{{cite journal}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Faworsky, A. Y. (1913). "Über die Einwirkung von Phosphorhalogenverbindungen auf Ketone, Bromketone und Ketonalkohole". J. Prakt. Chem. (in German). 88 (1): 641–698. doi:10.1002/prac.19130880148.
- ^ Kurti 1 Czako 2, Laszlo 1 Barbara 2 (15 September 2005). Strategic Applications of Named Reactions in Organic Synthesis. Elsevier. pp. 164–165. ISBN 0-12-429785-4.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Akhrem, A A; Ustynyuk, T K; Titov, Yu A (30 September 1970). "The Favorskii Rearrangement". Russian Chemical Reviews. 39 (9): 732–746. Bibcode:1970RuCRv..39..732A. doi:10.1070/rc1970v039n09abeh002019. ISSN 0036-021X.
- ^ Wallach, O. (1918). "Zur Kenntnis der Terpene und der ätherischen Öle. Über das Verhalten zweifach gebromter hexacyclischer Ketone in Abhängigkeit von der Stellung der Bromatome". Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. (in German). 414 (3): 271–296. doi:10.1002/jlac.19184140303.
- ^ Wallach, O. (1918). "Zur Kenntnis der Terpene und der ätherischen Öle". Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. (in German). 414 (3): 296–366. doi:10.1002/jlac.19184140304.
- ^ Park, Chan-Ho; Givens, Richard S. (1997). "New Photoactivated Protecting Groups. 6. p-Hydroxyphenacyl: A Phototrigger for Chemical and Biochemical Probes". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119 (10): 2453–2463. doi:10.1021/ja9635589.
- ^ Givens, Richard S.; Heger, Dominik; Hellrung, Bruno; Kamdzhilov, Yavor; Mac, Marek; Conrad, Peter G.; Cope, Elizabeth; Lee, Jong I.; Mata-Segreda, Julio F.; Schowen, Richard L.; Wirz, Jakob (2008). "The Photo-Favorskii Reaction of p-Hydroxyphenacyl Compounds is Initiated by Water-Assisted, Adiabatic Extrusion of a Triplet Biradical". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130 (11): 3307–3309. doi:10.1021/ja7109579. PMC 3739295. PMID 18290649.
- ^ Eaton, Philip E.; Cole, Thomas W. (1964). "Cubane". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 86 (15): 3157–3158. doi:10.1021/ja01069a041.
Further reading
- Chenier, Philip J. (1978). "Favorskii rearrangement in bridged polycyclic compounds". Journal of Chemical Education. 55 (5): 286. Bibcode:1978JChEd..55..286C. doi:10.1021/ed055p286.