Filling factor
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
Filling factor, , is a quantity measuring the efficiency of absorption of pump in the core of a double-clad fiber.[1][2][3]
Definition
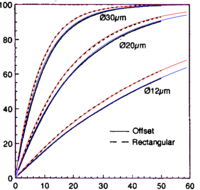
The efficiency of absorption of pumping energy in the fiber is an important parameter of a double-clad fiber laser. In many cases this efficiency can be approximated with[4]
where
- is the cross-sectional area of the cladding
- is the radius of the core (which is taken to be circular)
- is the absorption coefficient of pump light in the core
- is the length of the double-clad fiber, and
- is a dimensionless adjusting parameter, which is sometimes called the "filling factor"; .
The filling factor may depend on the initial distribution of the pump light, the shape of the cladding, and the position of the core within it.
Application
The large (close to unity) filling factor is important in double-clad amplifiers; it allows them to reduce the requirements for the brightness of the pump and to reduce the length of the fiber laser. Such a reduction is especially important for the power scaling of various nonlinear processes, and contributions of stimulated scattering to the degradation of signal. Use of the filling factor for the estimate of the efficiency of absorption of the pump in fiber lasers allows quick estimates without performing complicated numerical simulations.
See also
Notes
- ^ D. Kouznetsov, J. V. Moloney. Efficiency of pump in the double-clad fiber amplifiers. 2. Broken circular symmetry. JOSA B, 19, No.6, p.1259-1263 (2002). [1]
- ^ D. Kouznetsov, J. V. Moloney. Efficiency of pump absorption in double-clad fibers amplifiers. 3. Calculation of modes. JOSA B, 19, No.6, p.1304-1309 (2002). [2]
- ^ D. Kouznetsov, J. V. Moloney. Highly efficient, high gain, short wavelength and power scalable incoherent diode slab-pumped fiber laser amplifier. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, v.39, No.11, p.1452-1461 (2003). [3]
- ^ a b Kouznetsov, D.; Moloney, J.V. (2003). "Highly efficient, high-gain, short-length, and power-scalable incoherent diode slab-pumped fiber amplifier/laser". IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics. 39 (11): 1452–1461. Bibcode:2003IJQE...39.1452K. doi:10.1109/JQE.2003.818311.
- ^ A. Liu; K. Ueda (1996). "The absorption characteristics of circular, offset, and rectangular double-clad fibers". Optics Communications. 132 (5–6): 511–518. Bibcode:1996OptCo.132..511A. doi:10.1016/0030-4018(96)00368-9.









