Fixed end moment
The fixed end moments are reaction moments developed in a beam member under certain load conditions with both ends fixed. A beam with both ends fixed is statically indeterminate to the 3rd degree, and any structural analysis method applicable on statically indeterminate beams can be used to calculate the fixed end moments.
Many structural analysis methods including the moment distribution method, slope deflection method and the matrix method make use of the fixed end moments.
Examples
In the following examples, clockwise moments are positive. The vertical reactions are not shown since they can be easily determined from statics.
 Concentrated load of magnitude P |
 Linearly distributed load of maximum intensity q0 |
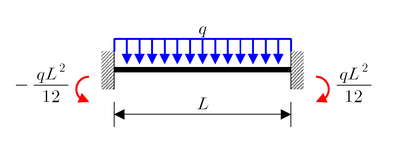 Uniformly distributed load of intensity q |
 Couple of magnitude M0 |
The two cases with distributed loads can be derived from the case with concentrated load by integration. For example, when a uniformly distributed load of intensity is acting on a beam, then an infinitely small part distance apart from the left end of this beam can be seen as being under a concentrated load of magnitude . Then,
Where the expressions within the integrals on the right hand sides are the fixed end moments caused by the concentrated load .
For the case with linearly distributed load of maximum intensity ,
See also
References
- Yang, Chang-hyeon (2001-01-10). Structural Analysis (in Korean) (4th ed.). Seoul: Cheong Moon Gak Publishers. ISBN 89-7088-709-1.
External Links









