Hypoglossal nucleus
| Hypoglossal nucleus | |
|---|---|
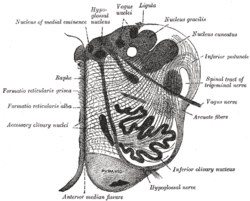 Section of the medulla oblongata at about the middle of the olive. (Hypoglossal nucleus visible top left.) | |
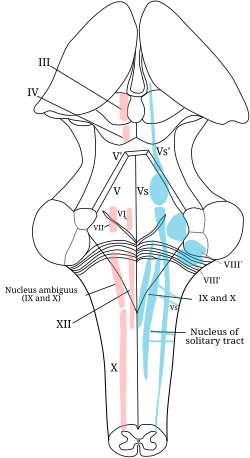 The cranial nerve nuclei schematically represented; dorsal view. Motor nuclei in red; sensory in blue. (XII labeled at bottom left.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nucleus nervi hypoglossi |
| NeuroNames | 757 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_2644 |
| TA98 | A14.1.04.227 |
| TA2 | 6010 |
| FMA | 54505 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The hypoglossal nucleus is a cranial nerve nucleus, and it extends the length of the medulla, and being a motor nucleus, is close to the midline. In the open medulla, it is visible as what is known as the hypoglossal trigone, a raised area (medial to the vagal trigone) protruding slightly into the fourth ventricle.
In the closed medulla, the gracile and cuneate nuclei lie posteriorly, which means the nucleus is not as close to the back of the medulla as in the open medulla. It is, however, still close to the midline.
See also
Additional images
-
Transverse section of medulla oblongata below the middle of the olive.
-
Nuclei of origin of cranial motor nerves schematically represented; lateral view.
-
Micrograph showing the hypoglossal nuclei in relation to their surrounding structures.
-
Micrograph showing the hypoglossal nucleus. H&E-LFB stain.
External links
- Atlas image: n2a6p2 at the University of Michigan Health System
- Stained brain slice images which include the "Hypoglossal nucleus" at the BrainMaps project
- NIF Search - Hypoglossal Nucleus via the Neuroscience Information Framework




