Ice rise
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2015) |
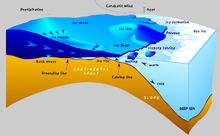
An ice rise is a clearly defined elevation of the otherwise totally flat ice shelf, typically dome-shaped and rising 100 to 200 metres above the surrounding ice shelf. An ice rise forms where the ice shelf touches the rocky seabed because of an elevation in the seabed that remains below sea level. (In contrast, an elevation in the seabed that extends above sea level is defined as an island). The ice shelf flows over the seabed elevation, completely covering it with ice, thereby forming an ice rise. The resulting tension forms crevasses around the ice rise.
An island within and totally covered by the ice shelf, may appear the exactly the same as an ice rise. Elaborate measurements may be required to distinguish between these two geographic features.
Although ice rises are typically located within the ice shelf area, they can partially face the open sea. Ice rises are found only on the ice shelves of Antarctica. The largest ice rises exceed dimensions of 50 by 200 km, or 10 000 km² in area. Some ice rises are incorrectly called islands, but also a few totally ice-covered islands within an ice shelf are also called ice rises.
Ice rises, grouped by ice shelf, clockwise starting in East Antarctica:
- Brunt Ice Shelf
- Riiser-Larsen Ice Shelf
- Amery Ice Shelf
- Budd Ice Rumples
- IR1 to IR5 near the ice front[1]
- Shackleton Ice Shelf
- Green Ice Rises (the northernmost ice rise, at 66°21'S)
- Harrisson Ice Rises
- Ross Ice Shelf
- Crary Ice Rise (the southernmost ice rise, at 82°56'S)
- Crosson Ice Shelf
- Bach Ice Shelf
- George VI Ice Shelf
- Wilkins Ice Shelf
- Wordie Ice Shelf
- Müller Ice Shelf
- Larsen-C Ice Shelf
- Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf
Henry and Korff Ice Rises are the largest ice rises, with areas of roughly 1 500 to 1 600 km².
References
- ^ Fricker et al., 2009, doi:10.1017/S095410200999023X
