Inyo Mountains
| Inyo Mountains | |
|---|---|
 Inyo Mountains from space | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Waucoba Mountain[1][2], ~18 mi (29 km) southeast of Big Pine. |
| Elevation | 11,123 ft (3,390 m) |
| Coordinates | 36°10′00″N 118°00′03″W / 36.16667°N 118.00083°W |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 70 mi (110 km) |
| Width | 10 mi (16 km) |
| Geography | |
| Country | United States |
| States | California and Nevada |
| Parent range | Basin and Range Province |
| Borders on | White Mountains, Sierra Nevada |
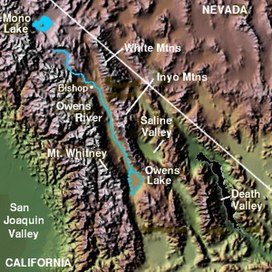
The Inyo Mountains are a short mountain range east of the Sierra Nevada mountains in eastern California in the United States.[3] The range separates the Owens Valley to the west from Saline Valley to the east, extending for approximately 70 mi (130 km) SSE from the southern end of the White Mountains, from which they are separated by Westgard Pass, to east of Owens Lake.
Geologically, the mountains are a fault block range in the Basin and Range Province, at the western end of the Great Basin. They are considered to be among the most important and best-known Late Proterozoic to Cambrian sections in the United States.[4]
Wilderness
Approximately 205,000 acres (830 km2) of the range are designated as the Inyo Mountain Wilderness managed by the Bureau of Land Management.[2] Much of the northern part of the range is within Inyo National Forest.
Wildlife in the area includes the endangered Inyo Mountains Salamander and the Desert Bighorn Sheep.[5] Plant communities include creosote and sagebrush at lower altitudes, and bristlecone pine forests at higher.[2] A number of rare and endemic plants are adapted to the unique limestone soils of the mountains, including the cliffdweller,[6] bristlecone cryptantha,[7] and Inyo rock daisy.[8]
References
- ^ "Waucoba Mountain". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2009-05-03.
- ^ a b c Gorp Destinations: Inyo Mountains Wilderness
- ^ "Inyo Mountains". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2009-05-03.
- ^ Localities of the Cambrian: White-Inyo Mountains
- ^ BLM: Inyo Mountain Wilderness
- ^ CNPS: Caulostramina
- ^ CNPS: Cryptantha roosiorum
- ^ CNPS: Perityle inyoensis
External links
- High Inyo Mountains Fossils, California
- Ammonoids At Union Wash, California Virtual field trip to a classic fossil locality along the western flanks of the Inyo Mountains
- Inyo Mountain Wilderness at BLM