J chain
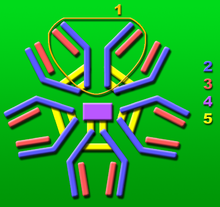
1: Base unit.
2: Heavy chains.
3: Light chains.
4: J chain.
5: Intermolecular disulfide bonds.

1: Heavy chains.
2: Light chains.
3: J-chain.
4: Secretory component.
A J chain is a protein component of the antibodies IgM and IgA.[1] It is a 137 residue polypeptide,[2] encoded by the IGJ gene.[3][4][5]
Structure
The J Chain's molecular weight is approximately 15 kDa. It exhibits a standard immunoglobulin folding structure of two β-pleated sheets of four ribbons folded against one another. It has 8 cystine residues. Two of these residues link the α chains of IgA or the μ chains of IgM via disulfide bridges, effectively serving as the "glue" between two Fc regions of the antibody.[6]
The J-chain shows a large degree of homology between avian and human species, suggesting that it serves an important function.[6]
Function
The J Chain is required for IgM or IgA to be secreted into mucosa.[2]
Because IgM and IgA are the only two types of antibody that polymerize, initial hypotheses stated that J chain was required for polymerization. However, it was subsequently found that IgM is able to polymerize in the absence of J chain as both a pentamer and a hexamer, however, both of these exist to lesser numbers in organisms lacking J chains. In such cases, there are also fewer IgA dimers.[2]
References
- ^ Levinson. Medical Microbiology and Immunology (11 ed.). McGrawHill. pp. 405–6.
- ^ a b c Schroeder, Harry; Wald, David; Greenspan, Neil (2008). "Chapter 4: Immunoglobulins: Structure and Function". In Paul, William (ed.). Fundamental Immunology (Book) (6th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 125–151. ISBN 0-7817-6519-6.
- ^ Max EE, McBride OW, Morton CC, Robinson MA (Sep 1986). "Human J chain gene: chromosomal localization and associated restriction fragment length polymorphisms". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 83 (15): 5592–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.15.5592. PMC 386334. PMID 3016707.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Max EE, Korsmeyer SJ (May 1985). "Human J chain gene. Structure and expression in B lymphoid cells". J Exp Med. 161 (4): 832–49. doi:10.1084/jem.161.4.832. PMC 2189063. PMID 2984306.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: IGJ immunoglobulin J polypeptide, linker protein for immunoglobulin alpha and mu polypeptides".
- ^ a b Kiyono, Hiroshi; Kunisawa, Jaw; McGhee, Jerry; Mestecky, Jiri (2008). "Chapter 31: The Mucosal Immune System". In Paul, William (ed.). Fundamental Immunology (Book) (6th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 983–1030. ISBN 0-7817-6519-6.
